Page 201 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 201
1. Conduct a the in the grid to inform your answers to some of the questions that follow.
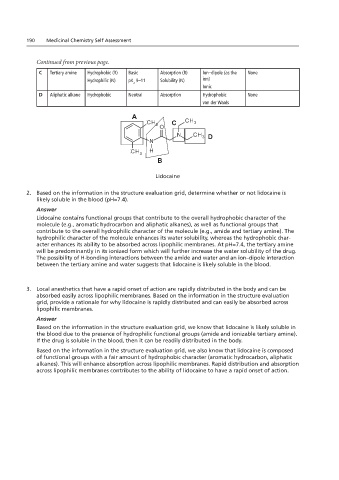
CH 3 CH 3
O
N CH
190 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment N 3
CH 3 H
Continued from previous page.
Absorption (R)
C Tertiary amine Hydrophobic (R) Basic Lidocaine Ion–dipole (as the None
Hydrophilic (N) pK 9–11 Solubility (N) ion)
a
Ionic
Answer:
D Aliphatic alkane Hydrophobic Neutral Absorption Hydrophobic None
van der Waals
A
C
D
B
Lidocaine
Lidocaine
2. Based on the information in the structure evaluation grid, determine whether or not lidocaine is
likely soluble in the blood (pH=7.4).
2. Based on the information in the
Answer
3. Local anesthetics that have.
Lidocaine contains functional groups that contribute to the overall hydrophobic character of the
molecule (e.g., aromatic hydrocarbon and aliphatic alkanes), as well as functional groups that
contribute to the overall hydrophilic character of the molecule (e.g., amide and tertiary amine). The
hydrophilic character of the molecule enhances its water solubility, whereas the hydrophobic char-
acter enhances its ability to be absorbed across lipophilic membranes. At pH=7.4, the tertiary amine
will be predominantly in its ionized form which will further increase the water solubility of the drug.
The possibility of H-bonding interactions between the amide and water and an ion–dipole interaction
between the tertiary amine and water suggests that lidocaine is likely soluble in the blood.
3. Local anesthetics that have a rapid onset of action are rapidly distributed in the body and can be
absorbed easily across lipophilic membranes. Based on the information in the structure evaluation
grid, provide a rationale for why lidocaine is rapidly distributed and can easily be absorbed across
lipophilic membranes.
Answer
Based on the information in the structure evaluation grid, we know that lidocaine is likely soluble in
the blood due to the presence of hydrophilic functional groups (amide and ionizable tertiary amine).
If the drug is soluble in the blood, then it can be readily distributed in the body.
Based on the information in the structure evaluation grid, we also know that lidocaine is composed
of functional groups with a fair amount of hydrophobic character (aromatic hydrocarbon, aliphatic
alkanes). This will enhance absorption across lipophilic membranes. Rapid distribution and absorption
across lipophilic membranes contributes to the ability of lidocaine to have a rapid onset of action.