Page 212 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 212
2.21 Phenobarbital and Other Barbiturates 201
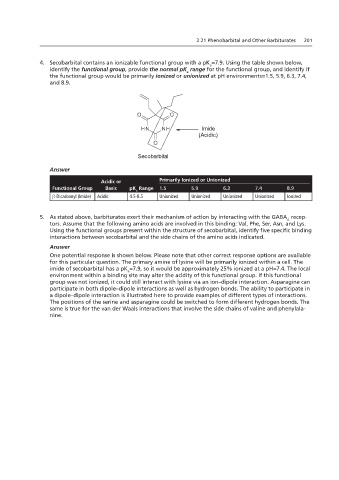
4. Secobarbital contains an ionizable functional group with a pK =7.9. Using the table shown below,
a
identify the functional group, provide the normal pK range for the functional group, and identify if
a
4. Secobarbital be primarily ionized or unionized at pH environments of 1.5, 5.9, 6.3, 7.4, and 8.9.
the functional group would be primarily ionized or unionized at pH environments=1.5, 5.9, 6.3, 7.4,
and 8.9.
Imide
(Acidic)
Secobarbital
Answer
5. As stated above between secobarbital and the side chains of the amino acids indicated.
Acidic or Primarily Ionized or Unionized
Answer:
Functional Group Basic pK Range 1.5 5.9 6.3 7.4 8.9
a
One that involve the side chains of valine and phenylalanine. Unionized Unionized Ionized
Acidic
Unionized
Unionized
β-Dicarbonyl (Imide)
4.5-8.5
<Production—Please change hyphens to n dashes for Dipole-Dipole in figure}
5. As stated above, barbiturates exert their mechanism of action by interacting with the GABA recep-
A
tors. Assume that the following amino acids are involved in this binding: Val, Phe, Ser, Asn, and Lys.
Using the functional groups present within the structure of secobarbital, identify five specific binding
van der Waals
Phe
interactions between secobarbital and the side chains of the amino acids indicated.
O
R 4
Answer NH Hydrophobic Interaction
R 3
One potential response is shown below. Please note that other correct response options are available
for this particular question. The primary amine of lysine will be primarily ionized within a cell. The
imide of secobarbital has a pK =7.9, so it would be approximately 25% ionized at a pH=7.4. The local
O
a
environment within a binding site may alter the acidity of this functional group. If this functional
Asn
R 2
group was not ionized, it could still interact with lysine via an ion–dipole interaction. Asparagine can
R 1
participate in both dipole–dipole interactions as well as hydrogen bonds. The ability to participate in
N
van der Waals
R 5
H
a dipole–dipole interaction is illustrated here to provide examples of different types of interactions.
Hydrophobic Interaction
Dipole-Dipole
The positions of the serine and asparagine could be switched to form different hydrogen bonds. The
O
O
O
O
Interaction
same is true for the van der Waals interactions that involve the side chains of valine and phenylala-
N
H
Val
NH
nine. 2 N N – R 6
H
O H + N
H 3 Ionic Bond
R 10 N O H
R 7
Hydrogen Bond O Lys
Ser H N O
R 9
R 8