Page 213 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 213
4. Secobarbital be primarily ionized or unionized at pH environments of 1.5, 5.9, 6.3, 7.4, and 8.9.
Imide
Secobarbital (Acidic)
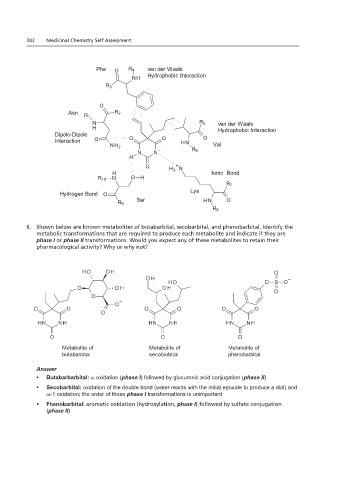
5. As stated above between secobarbital and the side chains of the amino acids indicated.
Answer:
One that involve the side chains of valine and phenylalanine.
<Production—Please change hyphens to n dashes for Dipole-Dipole in figure}
202 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Phe O R 4 van der Waals
NH Hydrophobic Interaction
R 3
O
Asn R 2
R 1
N R 5 van der Waals
H Hydrophobic Interaction
Dipole-Dipole
Interaction O O O H N O
NH 2 Val
N N – R 6
H
O H + N
H 3 Ionic Bond
R 10 N O H
R 7
Hydrogen Bond O Lys
Ser H N O
R 9
R 8
Chapters 1.21 and 2.21
6. Shown below are known metabolites of butabarbital, secobarbital, and phenobarbital. Identify the
Please replace the indicated structure in Question 6 in both 1.21 and 2.21 (the one that is part of the question)
metabolic transformations that are required to produce each metabolite and indicate if they are
phase I or phase II transformations. Would you expect any of these metabolites to retain their
with the one below. Both structures had an identical error.
pharmacological activity? Why or why not?
Metabolite of Metabolite of Metabolite of
butabarbital secobarbital phenobarbital
Answer
• Butabarbarbital: ω oxidation (phase I) followed by glucuronic acid conjugation (phase II)
• Secobarbital: oxidation of the double bond (water reacts with the initial epoxide to produce a diol) and
ω-1 oxidation; the order of these phase I transformations is unimportant
Chapter 2.22
• Phenobarbital: aromatic oxidation (hydroxylation, phase I) followed by sulfate conjugation
Please replace the structure for the answer to Question 3 in Chapter 2.22 with the one below.
(phase II)
Intramolecular
Hydrogen Bond
Intramolecular
Hydrogen Bond
Pravastatin
Fluvastatin