Page 217 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 217
2.22 Pravastatin and Fluvastatin
206 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
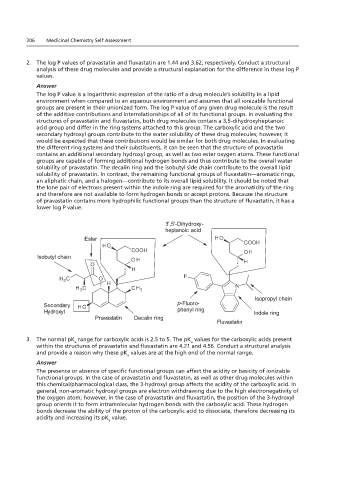
Shown below are the structures of pravastatin. A total of six functional groups have been boxed.
2. The log P values of pravastatin and fluvastatin are 1.44 and 3.62, respectively. Conduct a structural
F
analysis of these drug molecules and provide a structural explanation for the difference in these log P
C
values.
Answer
The log P value is a logarithmic expression of the ratio of a drug molecule’s solubility in a lipid
B
D
environment when compared to an aqueous environment and assumes that all ionizable functional
groups are present in their unionized form. The log P value of any given drug molecule is the result
A
of the additive contributions and interrelationships of all of its functional groups. In evaluating the
structures of pravastatin and fluvastatin, both drug molecules contain a 3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic
acid group and differ in the ring systems attached to this group. The carboxylic acid and the two
secondary hydroxyl groups contribute to the water solubility of these drug molecules; however, it
E
would be expected that these contributions would be similar for both drug molecules. In evaluating
the different ring systems and their substituents, it can be seen that the structure of pravastatin
Pravastatin
contains an additional secondary hydroxyl group, as well as two ester oxygen atoms. These functional
Fluvastatin
groups are capable of forming additional hydrogen bonds and thus contribute to the overall water
solubility of pravastatin. The decalin ring and the isobutyl side chain contribute to the overall lipid
solubility of pravastatin. In contrast, the remaining functional groups of fluvastatin—aromatic rings,
1. Using the table below, drophilic or hydrophobic in character. for your response.
an aliphatic chain, and a halogen—contribute to its overall lipid solubility. It should be noted that
2. The log P values of s and provide a structural explanation for the difference in these log P values.
the lone pair of electrons present within the indole ring are required for the aromaticity of the ring
and therefore are not available to form hydrogen bonds or accept protons. Because the structure
Answer
of pravastatin contains more hydrophilic functional groups than the structure of fluvastatin, it has a
The log P value is a functional groups than the structure of fluvastatin, it has a lower log P value.
lower log P value.
3',5'-Dihydroxy-
heptanoic acid
Ester
Isobutyl chain
Isopropyl chain
Secondary p-Fluoro-
Hydroxyl phenyl ring Indole ring
Pravastatin Decalin ring
Fluvastatin
3. The normal pK range for carboxylic acids is 2.5 to 5. The pK values for the carboxylic acids present
a
a
within the structures of pravastatin and fluvastatin are 4.21 and 4.56. Conduct a structural analysis
and provide a reason why these pK values are at the high end of the normal range.
a
Answer
The presence or absence of specific functional groups can affect the acidity or basicity of ionizable
functional groups. In the case of pravastatin and fluvastatin, as well as other drug molecules within
this chemical/pharmacological class, the 3-hydroxyl group affects the acidity of the carboxylic acid. In
general, non-aromatic hydroxyl groups are electron withdrawing due to the high electronegativity of
the oxygen atom; however, in the case of pravastatin and fluvastatin, the position of the 3-hydroxyl
group orients it to form intramolecular hydrogen bonds with the carboxylic acid. These hydrogen
bonds decrease the ability of the proton of the carboxylic acid to dissociate, therefore decreasing its
acidity and increasing its pK value.
a