Page 219 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 219
Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
208 Answer
Answer
In the reaction most likely occupy binding sites that are adjacent to the active site of the enzyme.
In the reaction most likely occupy binding sites that are adjacent to the active site of the enzyme.
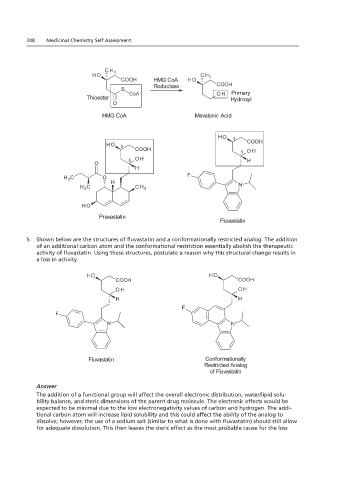
HMG CoA
HMG CoA
Reductase
Reductase Primary
Thioester Hydroxyl
Primary
Thioester Hydroxyl
HMG CoA Mevalonic Acid
HMG CoA Mevalonic Acid
H O 3
H O 3 H O 3 COOH
COOH
H O 3 COOH 5 OH
COOH
O 5 OH OH H 5 OH
H
O H 5
H F
H 3 C O F
H 3 C H C H O H CH N
3
3
H 3 C CH 3 N
H O
H O
Pravastatin
Pravastatin Fluvastatin
Fluvastatin
5. Shown below are the structures of fluvastatin and a conformationally restricted analog. The addition
of an additional carbon atom and the conformational restriction essentially abolish the therapeutic
5. Shown below are the structures why this structural change results in a loss in activity.
activity of fluvastatin. Using these structures, postulate a reason why this structural change results in
5. Shown below are the structures why this structural change results in a loss in activity.
a loss in activity.
Fluvastatin Conformationally
Conformationally
Fluvastatin Restricted Analog
Restricted Analog
of Fluvastatin
of Fluvastatin
Answer
The addition of a functional group will affect the overall electronic distribution, water/lipid solu-
bility balance, and steric dimensions of the parent drug molecule. The electronic effects would be
expected to be minimal due to the low electronegativity values of carbon and hydrogen. The addi-
tional carbon atom will increase lipid solubility and this could affect the ability of the analog to
dissolve; however, the use of a sodium salt (similar to what is done with fluvastatin) should still allow
for adequate dissolution. This then leaves the steric effect as the most probable cause for the loss