Page 224 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 224
Chapter 1.23
Please replace the structure for Question 2 in Chapter 1.23 with the one shown below. (NOTE: The analogous
structure in Chapter 2.23 is fine.)
2.23 Quinapril 213
Chapters 1.23 and 2.23
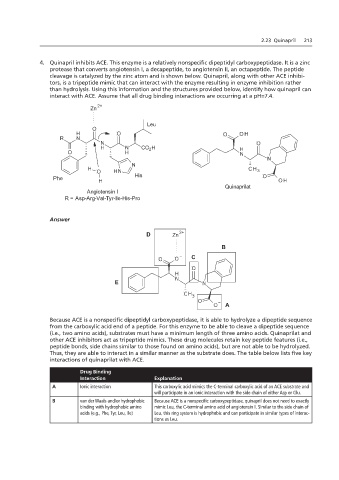
4. Quinapril inhibits ACE. This enzyme is a relatively nonspecific dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase. It is a zinc
Please replace the structures for Angiotensin I and Quinaprilat in Question 4 for both 1.23 and 2.23 with the
protease that converts angiotensin I, a decapeptide, to angiotensin II, an octapeptide. The peptide one
cleavage is catalyzed by the zinc atom and is shown below. Quinapril, along with other ACE inhibi-
provided below.
4. Quinapril inhibits ACE. binding interactions are occurring at a pH of 7.4.
tors, is a tripeptide mimic that can interact with the enzyme resulting in enzyme inhibition rather
than hydrolysis. Using this information and the structures provided below, identify how quinapril can
interact with ACE. Assume that all drug binding interactions are occurring at a pH=7.4.
Leu
Leu
Phe His
Phe His Quinaprilat
Angiotensin I Quinaprilat
R = Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His
Angiotensin I
R = Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro
Answer
Answer
D
B
C
E
A
Because ACE is a nonspecific dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase, it is able to hydrolyze a dipeptide sequence
from the carboxylic acid end of a peptide. For this enzyme to be able to cleave a dipeptide sequence
(i.e., two amino acids), substrates must have a minimum length of three amino acids. Quinaprilat and
other ACE inhibitors act as tripeptide mimics. These drug molecules retain key peptide features (i.e.,
peptide bonds, side chains similar to those found on amino acids), but are not able to be hydrolyzed.
Thus, they are able to interact in a similar manner as the substrate does. The table below lists five key
interactions of quinaprilat with ACE.
Drug Binding
Interaction Explanation
A Ionic interaction This carboxylic acid mimics the C-terminal carboxylic acid of an ACE substrate and
will participate in an ionic interaction with the side chain of either Asp or Glu.
B van der Waals and/or hydrophobic Because ACE is a nonspecific carboxypeptidase, quinapril does not need to exactly
binding with hydrophobic amino mimic Leu, the C-terminal amino acid of angiotensin I. Similar to the side chain of
acids (e.g., Phe, Tyr, Leu, Ile) Leu, this ring system is hydrophobic and can participate in similar types of interac-
tions as Leu.