Page 225 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 225
214 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Continued from previous page.
C Hydrogen bond acceptor Because ACE is a dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase, it does not cleave the terminal
peptide bond. Instead, the terminal peptide bond can participate in hydrogen
bonds. The carbonyl of the amide bond can act as a hydrogen bond acceptor and
interact with Ser, Thr, Tyr, Trp, Gln, Asn, or Cys.
D Ionic bond (metal complexation) This carboxylic acid would be located very close to the zinc atom shown partici-
pating in the mechanism of angiotensin I metabolism. As such, at pH=7 it can
form an ionic bond with the zinc atom.
E van der Waals and/or hydrophobic This aromatic ring mimics the Phe side chain of angiotensin I and can participate
binding with hydrophobic amino in similar interactions.
acids (e.g., Phe, Tyr, Trp)
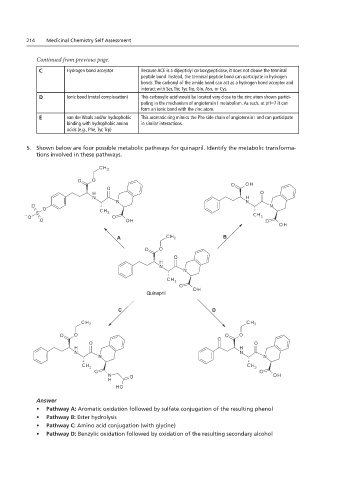
5. Shown below are in these pathways.
5. Shown below are four possible metabolic pathways for quinapril. Identify the metabolic transforma-
Answer
tions involved in these pathways.
A B
Quinapril
C D
Answer
• Pathway A: Aromatic oxidation followed by sulfate conjugation of the resulting phenol
• Pathway B: Ester hydrolysis
• . Pathway C: Amino acid conjugation (with glycine)
• Pathway D: Benzylic oxidation followed by oxidation of the resulting secondary alcohol