Page 230 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 230
2.24 Rivastigmine 219
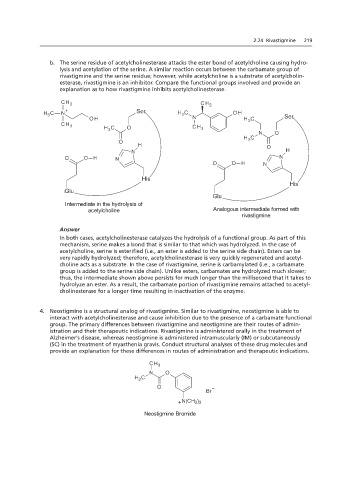
b. The serine residue of acetylcholinesterase attacks the ester bond of acetylcholine causing hydro-
lysis and acetylation of the serine. A similar reaction occurs between the carbamate group of
rivastigmine and the serine residue; however, while acetylcholine is a substrate of acetylcholin-
B.
The serine residue inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
esterase, rivastigmine is an inhibitor. Compare the functional groups involved and provide an
explanation as to how rivastigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
B. The serine residue inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
Intermediate in the hydrolysis of
acetylcholine Analogous intermediate formed with
rivastigmine
Answer
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog in routes of administration.
In both cases, acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the hydrolysis of a functional group. As part of this
mechanism, serine makes a bond that is similar to that which was hydrolyzed. In the case of
acetylcholine, serine is esterified (i.e., an ester is added to the serine side chain). Esters can be
very rapidly hydrolyzed; therefore, acetylcholinesterase is very quickly regenerated and acetyl-
choline acts as a substrate. In the case of rivastigmine, serine is carbamylated (i.e., a carbamate
group is added to the serine side chain). Unlike esters, carbamates are hydrolyzed much slower;
thus, the intermediate shown above persists for much longer than the millisecond that it takes to
+
hydrolyze an ester. As a result, the carbamate portion of rivastigmine remains attached to acetyl-
cholinesterase for a longer time resulting in inactivation of the enzyme.
Neostigmine Bromide
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog of rivastigmine. Similar to rivastigmine, neostigmine is able to
interact with acetylcholinesterase and cause inhibition due to the presence of a carbamate functional
Intermediate in the hydrolysis of
5. Rivastigmine has a difference results in a longer duration of action.
group. The primary differences between rivastigmine and neostigmine are their routes of admin-
Analogous intermediate formed with
acetylcholine
istration and their therapeutic indications. Rivastigmine is administered orally in the treatment of
rivastigmine
Alzheimer’s disease, whereas neostigmine is administered intramuscularly (IM) or subcutaneously
Methyl
(SC) in the treatment of myasthenia gravis. Conduct structural analyses of these drug molecules and
Methyl
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog in routes of administration.
provide an explanation for these differences in routes of administration and therapeutic indications.
Methyl
Ethyl
+
Neostigmine Rivastigmine
+
Neostigmine Bromide
5. Rivastigmine has a difference results in a longer duration of action.
Methyl
Methyl
Methyl
Ethyl
+
Neostigmine Rivastigmine