Page 231 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 231
B.
The serine residue inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
Intermediate in the hydrolysis of
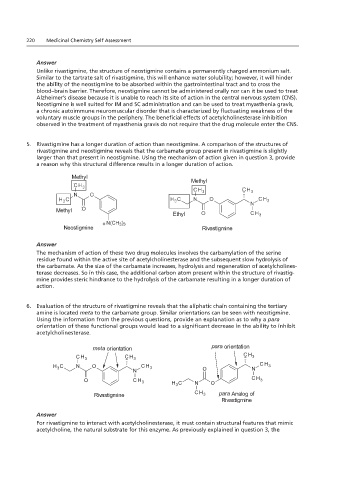
220 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
acetylcholine Analogous intermediate formed with
rivastigmine
Answer
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog in routes of administration.
Unlike rivastigmine, the structure of neostigmine contains a permanently charged ammonium salt.
Similar to the tartrate salt of rivastigmine, this will enhance water solubility; however, it will hinder
the ability of the neostigmine to be absorbed within the gastrointestinal tract and to cross the
blood–brain barrier. Therefore, neostigmine cannot be administered orally nor can it be used to treat
Alzheimer’s disease because it is unable to reach its site of action in the central nervous system (CNS).
Neostigmine is well suited for IM and SC administration and can be used to treat myasthenia gravis,
a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disorder that is characterized by fluctuating weakness of the
voluntary muscle groups in the periphery. The beneficial effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibition
+
observed in the treatment of myasthenia gravis do not require that the drug molecule enter the CNS.
Neostigmine Bromide
5. Rivastigmine has a longer duration of action than neostigmine. A comparison of the structures of
rivastigmine and neostigmine reveals that the carbamate group present in rivastigmine is slightly
larger than that present in neostigmine. Using the mechanism of action given in question 3, provide
5. Rivastigmine has a difference results in a longer duration of action.
a reason why this structural difference results in a longer duration of action.
Methyl
Methyl
Methyl
Ethyl
+
Neostigmine Rivastigmine
Answer
The mechanism of action of these two drug molecules involves the carbamylation of the serine
residue found within the active site of acetylcholinesterase and the subsequent slow hydrolysis of
the carbamate. As the size of the carbamate increases, hydrolysis and regeneration of acetylcholines-
terase decreases. So in this case, the additional carbon atom present within the structure of rivastig-
mine provides steric hindrance to the hydrolysis of the carbamate resulting in a longer duration of
action.
6. Evaluation of the structure of rivastigmine reveals that the aliphatic chain containing the tertiary
amine is located meta to the carbamate group. Similar orientations can be seen with neostigmine.
Using the information from the previous questions, provide an explanation as to why a para
orientation of these functional groups would lead to a significant decrease in the ability to inhibit
6. Evaluation of the to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
acetylcholinesterase.
meta orientation para orientation
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
H C N O CH 3 CH 3
3
N O N
O CH 3 H 3 C N O CH 3
Rivastigmine CH 3 para Analog of
Rivastigmine
Answer
Answer:
For rivastigmine to interact with acetylcholinesterase, it must contain structural features that mimic
For rivastigmine to interact with acetylcholinesterase, it must contain structural features that mimic
acetylcholine, the natural substrate for this enzyme. As previously explained in question 3, the
The meta orientation allows for similar distances
The para orientation places the functional groups
too far apart from one another