Page 236 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 236
2.25 Sitagliptin 225
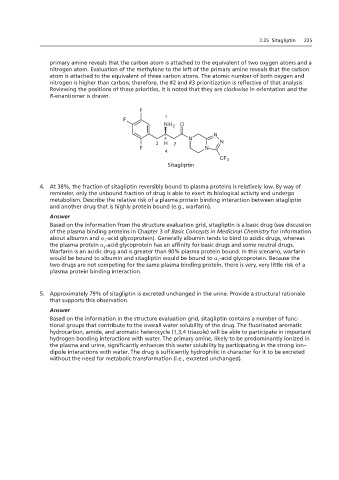
3. Sitagliptin is designation.
primary amine reveals that the carbon atom is attached to the equivalent of two oxygen atoms and a
Answer:
nitrogen atom. Evaluation of the methylene to the left of the primary amine reveals that the carbon
atom is attached to the equivalent of three carbon atoms. The atomic number of both oxygen and
Using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (are clockwise in orientation and the R-enantiomer is drawn.
nitrogen is higher than carbon; therefore, the #2 and #3 prioritization is reflective of that analysis.
Reviewing the positions of these priorities, it is noted that they are clockwise in orientation and the
R-enantiomer is drawn.
1
3 2
4
Sitagliptin
Sitagliptin
4. At 38%, the fraction of sitagliptin reversibly bound to plasma proteins is relatively low. By way of
4. At 38%, the bound (e.g., warfarin).
reminder, only the unbound fraction of drug is able to exert its biological activity and undergo
metabolism. Describe the relative risk of a plasma protein binding interaction between sitagliptin
5. Approximately 79% of urine. Provide a abolic transformation (i.e., excreted unchanged).
and another drug that is highly protein bound (e.g., warfarin).
Answer
Based on the information from the structure evaluation grid, sitagliptin is a basic drug (see discussion
6. Assess each of the liptin and determine which phase I metabolic transformation has occurred.
of the plasma binding proteins in Chapter 3 of Basic Concepts in Medicinal Chemistry for information
about albumin and α -acid glycoprotein). Generally albumin tends to bind to acidic drugs, whereas
1
the plasma protein α -acid glycoprotein has an affinity for basic drugs and some neutral drugs.
1
Warfarin is an acidic drug and is greater than 90% plasma protein bound. In this scenario, warfarin
would be bound to albumin and sitagliptin would be bound to α -acid glycoprotein. Because the
1
two drugs are not competing for the same plasma binding protein, there is very, very little risk of a
plasma protein binding interaction.
5. Approximately 79% of sitagliptin is excreted unchanged in the urine. Provide a structural rationale
that supports this observation.
Answer
Based on the information in the structure evaluation grid, sitagliptin contains a number of func-
tional groups that contribute to the overall water solubility of the drug. The fluorinated aromatic
hydrocarbon, amide, and aromatic heterocycle (1,3,4 triazole) will be able to participate in important
hydrogen bonding interactions with water. The primary amine, likely to be predominantly ionized in
the plasma and urine, significantly enhances this water solubility by participating in the strong ion–
dipole interactions with water. The drug is sufficiently hydrophilic in character for it to be excreted
without the need for metabolic transformation (i.e., excreted unchanged).