Page 239 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 239
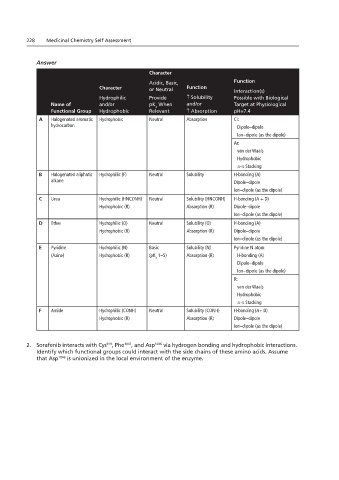
228 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Answer
Character
Acidic, Basic, Function
Character or Neutral Function Interaction(s)
Hydrophilic Provide ↑ Solubility Possible with Biological
Name of and/or pK When and/or Target at Physiological
a
Functional Group Hydrophobic Relevant ↑ Absorption pH=7.4
A Halogenated aromatic Hydrophobic Neutral Absorption Cl:
hydrocarbon Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the dipole)
Ar:
van der Waals
Hydrophobic
π-π Stacking
B Halogenated aliphatic Hydrophilic (F) Neutral Solubility H-bonding (A)
alkane Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the dipole)
C Urea Hydrophilic (HNCONH) Neutral Solubility (HNCONH) H-bonding (A + D)
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the dipole)
D Ether Hydrophilic (O) Neutral Solubility (O) H-bonding (A)
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the dipole)
E Pyridine Hydrophilic (N) Basic Solubility (N) Pyridine N atom:
(Azine) Hydrophobic (R) (pK 1–5) Absorption (R) H-bonding (A)
a
Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the dipole)
R:
van der Waals
Hydrophobic
π-π Stacking
F Amide Hydrophilic (CONH) Neutral Solubility (CONH) H-bonding (A+ D)
Hydrophobic (R) Absorption (R) Dipole–dipole
Ion–dipole (as the dipole)
2. Sorafenib interacts with Cys , Phe 1047 , and Asp 1046 via hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions.
919
Identify which functional groups could interact with the side chains of these amino acids. Assume
that Asp 1046 is unionized in the local environment of the enzyme.