Page 238 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 238
Section 4 Whole Molecule Drug Evaluation
Answers
2.26 Sorafenib
Because protein tyrosine kinases regulate cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival, it is no surprise that
several neoplastic disorders can be tied to altered activity of protein tyrosine kinases. Clinically relevant antineo-
plastic tyrosine kinase inhibitors interact with the active site of the enzyme via several types of binding interactions.
The adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding domain of the tyrosine kinases contains a hydrophobic domain that
includes a significant number of isoleucine, leucine, alanine and valine residues. There are at least five binding pockets
that flank this region in which van der Waals, hydrophobic, hydrogen bonding, and electrostatic interactions occur.
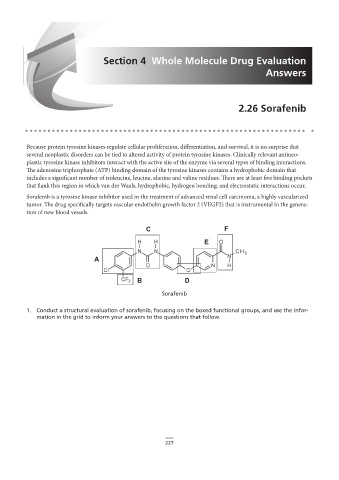
Sorafenib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma, a highly vascularized
2.26 Sorafenib
tumor. The drug specifically targets vascular endothelin growth factor 2 (VEGF2) that is instrumental in the genera-
tion of new blood vessels.
Because protein tyrosine kinases owth is instrumental in the generation of new blood vessels.
C F
E
A
B D
Sorafenib
Sorafenib
1. Conduct a structural evaluation of sorafenib, focusing on the boxed functional groups, and use the infor-
1. Conduct a to the questions that follow.
mation in the grid to inform your answers to the questions that follow.
2. Sorafenib interacts with in the local environment of the enzyme.
3. Nilotinib, another and Leu 298 /Val 299 /Phe 359 in each of the respective five binding pockets.
A
B C D E
Nilotinib
227
A. Consider the side chains of the. Assume pH=7.4.
B. Determine which of the side chains are both at pH=7.4.
C. It has been atom(s) within the structure of methionine participate in this interaction.
Methionine