Page 31 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 31
3. Each of the three odorant molecules drawn below produces a unique scent on interaction with the
olfactory receptors. Unlike most biological targets for drug action, olfactory receptors typically have an
physiological pH? Indicate which functional group(s) can participate in each of the interactions identified.
Sclareol Nerolidol
(herbal scent) Vanillin (green woody scent)
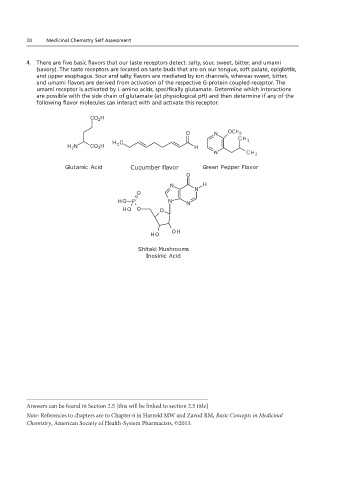
20 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
4. There are five basic flavors that our taste receptors detect: salty, sour, sweet, bitter, and umami
(savory). The taste receptors are located on taste buds that are on our tongue, soft palate, epiglottis,
and upper esophagus. Sour and salty flavors are mediated by ion channels, whereas sweet, bitter,
4. There are five basic flavors that our taste receptors detect: salty, sour, sweet, bitter, and umami
and umami flavors are derived from activation of the respective G-protein coupled receptor. The
(savory). The taste receptors are located on taste buds that are on our tongue, soft palate, epiglottis, and
umami receptor is activated by L-amino acids, specifically glutamate. Determine which interactions
are possible with the side chain of glutamate (at physiological pH) and then determine if any of the
following flavor molecules can interact with and activate this receptor.
CO H
2
H 2 N CO H
2
Glutamic Acid Cucumber flavor Green Pepper Flavor
O
N H
O N
H O P N N
H O O O
OH
H O
Shitaki Mushrooms
Inosinic Acid
Answers can be found in Section 2.5 [this will be linked to section 2.5 title]
Note: References to chapters are to Chapter 6 in Harrold MW and Zavod RM, Basic Concepts in Medicinal
Chemistry, American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, ©2013.