Page 33 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 33
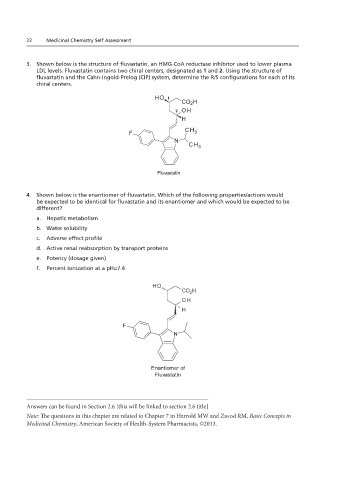
22 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
3. Shown below is the structure of fluvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor used to lower plasma LDL levels.
Fluvastatin contains two chiral centers, designated as A and B. Using the structure of fluvastatin and the Cahn-
Medicinal Chemistry Self-Assessment Book: Batch Two
3. Shown below is the structure of fluvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor used to lower plasma
Chapters 1.6 and 2.6
Ingold-Prelog (CIP) system, determine the R/S configurations for each of its chiral centers.
LDL levels. Fluvastatin contains two chiral centers, designated as 1 and 2. Using the structure of
fluvastatin and the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) system, determine the R/S configurations for each of its
Revised structure reflects chiral carbons #1 and #2.
chiral centers.
H O 1 A
CO 2 H
2 OH
B
H
F CH 3
N
CH 3
Fluvastatin
Fluvastatin
4. Shown below is the enantiomer of fluvastatin. Which of the following properties/actions would
be expected to be identical for fluvastatin and its enantiomer and which would be expected to be
4. Shown below is the enantiomer of fluvastatin. Which of the following properties/actions would be expected to
different?
a. Hepatic metabolism
be identical for fluvastatin and its enantiomer and which would be expected to be different?
b. Water solubility
a. Hepatic metabolism
c. Adverse effect profile
b. Water solubility
d. Active renal reabsorption by transport proteins
e. Potency (dosage given)
f. Percent ionization at a pH=7.4
Enantiomer of
Fluvastatin
Answers can be found in Section 2.6 [this will be linked to section 2.6 title]
Note: The questions in this chapter are related to Chapter 7 in Harrold MW and Zavod RM, Basic Concepts in
Medicinal Chemistry, American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, ©2013.
Page 2 of 2