Page 77 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 77
66 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
3. Local anesthetics that have a rapid onset of action are rapidly distributed in the body and can be
absorbed easily across lipophilic membranes. Based on the information in the structure evaluation
grid, provide a rationale for why lidocaine is rapidly distributed and can easily be absorbed across
lipophilic membranes.
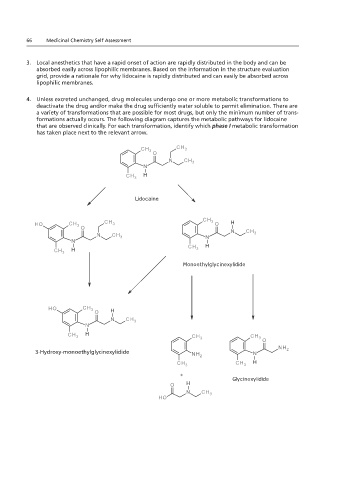
4. Unless excreted unchanged, drug molecules undergo one or more metabolic transformations to
deactivate the drug and/or make the drug sufficiently water soluble to permit elimination. There are
a variety of transformations that are possible for most drugs, but only the minimum number of trans-
1.19 and 2.19 – remove bold from labels and remove answers from over the arrows (pay no attention to
formations actually occurs. The following diagram captures the metabolic pathways for lidocaine
the colors)
that are observed clinically. For each transformation, identify which phase I metabolic transformation
has taken place next to the relevant arrow.
CH CH 3
3
O
N CH 3
N
CH 3 H
Lidocaine
H O CH CH 3 CH 3 O H
3
O N CH
N CH 3 N 3
N
CH H
CH 3 H 3
Monoethylglycinexylidide
H O CH 3
O H
N CH 3
N
CH 3 H CH CH
3
3
O
NH
3-Hydroxy-monoethylglycinexylidide NH 2 N 2
3-Hydroxy-monoethylglycineexylidide
CH 3 CH 3 H
+ Glycinexylidide
O H
N CH
H O 3