Page 91 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 91
1.24 Rivastigmine
Shown below is the structure of rivastigmine. Four of its functional groups have been identified.
CH
C
CH
D
3
3
1.24 Rivastigmine
A
CH
O
H
C
N
3
3
N
Shown below is the structure of rivastigmine. Four of its functional groups have been identified.
O CH
CH 3 C CH 3 D 3
B
A H 3 C N O Rivastigmine N CH 3
O CH 3
1. Using the table B
Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment Rivastigmine
80 2. Based on their induction.
3. Rivastigmine is an e. Glutamic acid, with acetylcholine.
1. Using the table
2. Based on their induction.
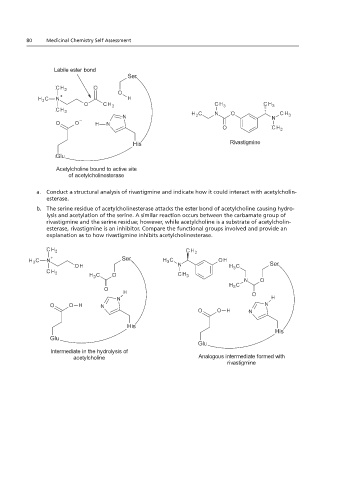
Labile ester bond
3. Rivastigmine is an e. Glutamic acid, with acetylcholine.
Labile ester bond
Rivastigmine
Acetylcholine bound to active site Rivastigmine
of acetylcholinesterase
A.
Conduct a rivastigmine and indicate how it could interact with acetylcholinestase.
a. Conduct a structural analysis of rivastigmine and indicate how it could interact with acetylcholin-
Acetylcholine bound to active site
esterase. The serine explanation as to how rivastigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
B.
of acetylcholinesterase
b. The serine residue of acetylcholinesterase attacks the ester bond of acetylcholine causing hydro-
lysis and acetylation of the serine. A similar reaction occurs between the carbamate group of
A.
Conduct a rivastigmine and indicate how it could interact with acetylcholinestase.
rivastigmine and the serine residue; however, while acetylcholine is a substrate of acetylcholin-
B.
The serine explanation as to how rivastigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
esterase, rivastigmine is an inhibitor. Compare the functional groups involved and provide an
explanation as to how rivastigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
Intermediate in the hydrolysis of
acetylcholine Analogous intermediate formed with
rivastigmine
Intermediate in the hydrolysis of
acetylcholine Analogous intermediate formed with
rivastigmine