Page 92 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 92
1.24 Rivastigmine 81
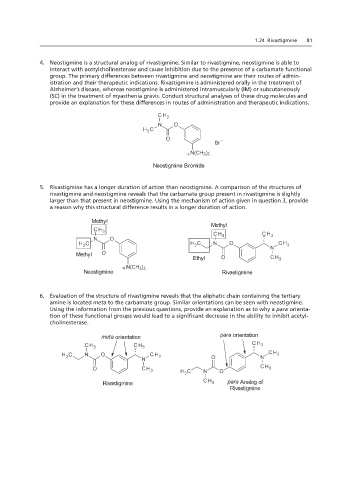
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog of rivastigmine. Similar to rivastigmine, neostigmine is able to
interact with acetylcholinesterase and cause inhibition due to the presence of a carbamate functional
group. The primary differences between rivastigmine and neostigmine are their routes of admin-
istration and their therapeutic indications. Rivastigmine is administered orally in the treatment of
Alzheimer’s disease, whereas neostigmine is administered intramuscularly (IM) or subcutaneously
(SC) in the treatment of myasthenia gravis. Conduct structural analyses of these drug molecules and
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog of es in routes of administration.
provide an explanation for these differences in routes of administration and therapeutic indications.
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog of es in routes of administration.
4. Neostigmine is a structural analog of es in routes of administration.
+
Neostigmine Bromide
+
Neostigmine Bromide
5. Rivastigmine has a longer duration of a longer duration of action.
5. Rivastigmine has a longer duration of action than neostigmine. A comparison of the structures of
rivastigmine and neostigmine reveals that the carbamate group present in rivastigmine is slightly
+
larger than that present in neostigmine. Using the mechanism of action given in question 3, provide
5. Rivastigmine has a longer duration of a longer duration of action.
Methyl
Neostigmine Bromide
a reason why this structural difference results in a longer duration of action.
Methyl
Methyl
Methyl
5. Rivastigmine has a longer duration of a longer duration of action.
Methyl
Methyl Ethyl Methyl
Methyl + Rivastigmine
Neostigmine
Ethyl
+
Neostigmine
Rivastigmine
6. Evaluation of the structure of rivastigmine ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
Methyl
Ethyl
6. Evaluation of the structure of rivastigmine ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
+
para orientation
meta orientation
Neostigmine
6. Evaluation of the structure of rivastigmine reveals that the aliphatic chain containing the tertiary
Rivastigmine
amine is located meta to the carbamate group. Similar orientations can be seen with neostigmine.
Using the information from the previous questions, provide an explanation as to why a para orienta-
para orientation
meta orientation
6. Evaluation of the structure of rivastigmine ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
tion of these functional groups would lead to a significant decrease in the ability to inhibit acetyl-
cholinesterase.
meta orientation para orientation
Rivastigmine para Analog of
Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine para Analog of
Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine para Analog of
Rivastigmine