Page 213 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 213
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
3. Fractional crystallization by cooling (for cryst. phenols)
4. Formation of phenolates (= phenates) with alkali which is water soluble.
N.B. Phenolic ethers are neutral compounds and do not react with alkalis but generate
phenols on heating with HI or HBr.
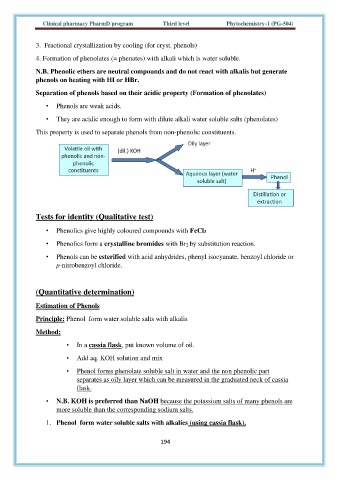
Separation of phenols based on their acidic property (Formation of phenolates)
• Phenols are weak acids.
• They are acidic enough to form with dilute alkali water soluble salts (phenolates)
This property is used to separate phenols from non-phenolic constituents.
Tests for identity (Qualitative test)
• Phenolics give highly coloured compounds with FeCl3
• Phenolics form a crystalline bromides with Br2 by substitution reaction.
• Phenols can be esterified with acid anhydrides, phenyl isocyanate, benzoyl chloride or
p-nitrobenzoyl chloride.
(Quantitative determination)
Estimation of Phenols
Principle: Phenol form water soluble salts with alkalis
Method:
• In a cassia flask, put known volume of oil.
• Add aq. KOH solution and mix
• Phenol forms phenolate soluble salt in water and the non phenolic part
separates as oily layer which can be measured in the graduated neck of cassia
flask.
• N.B. KOH is preferred than NaOH because the potassium salts of many phenols are
more soluble than the corresponding sodium salts.
1. Phenol form water soluble salts with alkalies (using cassia flask).
194