Page 58 - Data Science Algorithms in a Week
P. 58
42 Edwin Cortes, Luis Rabelo and Gene Lee
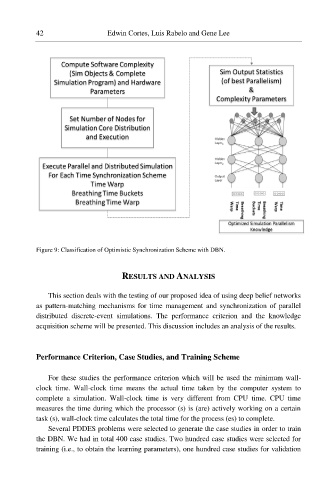
Figure 9: Classification of Optimistic Synchronization Scheme with DBN.
RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
This section deals with the testing of our proposed idea of using deep belief networks
as pattern-matching mechanisms for time management and synchronization of parallel
distributed discrete-event simulations. The performance criterion and the knowledge
acquisition scheme will be presented. This discussion includes an analysis of the results.
Performance Criterion, Case Studies, and Training Scheme
For these studies the performance criterion which will be used the minimum wall-
clock time. Wall-clock time means the actual time taken by the computer system to
complete a simulation. Wall-clock time is very different from CPU time. CPU time
measures the time during which the processor (s) is (are) actively working on a certain
task (s), wall-clock time calculates the total time for the process (es) to complete.
Several PDDES problems were selected to generate the case studies in order to train
the DBN. We had in total 400 case studies. Two hundred case studies were selected for
training (i.e., to obtain the learning parameters), one hundred case studies for validation