Page 20 - Insurance Times March 2021
P. 20
scale." Thus, enabling not just the larger carriers, but Let's categorise the gaps in four high level
carriers of all sizes. AI is nowhere yet close to the level categories and see how AI is enabling start-ups
where it can entirely replace humans, except in movies.
However, AI has now reached a level where it can be the to address these gaps:
best tool that humans can use to deliver their services Data Gaps: A data gap is created when some data fields
better. Insurance has the unique challenge of very low are needed for data analytics-based decisions but the insurer
customer engagement and customer loyalty. AI can be a is not able to capture them. Players are attempting to
great asset to enable insurers to engage with every single provide external data about the customers. They are
customer at a personalized level and create the much leveraging machine learning-based de-duplication and linking
needed connection - financially and emotionally. technologies to identify a unique customer and then provide
additional data about the data
subject from external data
sources. Some players are
helping insurers digitize their
internal data by improving
data capture at each stage of
insurance operations. For
example, optical character
recognition (OCR) and then
natural language processing
(NLP) are used to capture and
logically store data from
existing physical documents.
Process gaps: A process gap
is created when new
technologies having the
potential to transform one or
more steps in insurance value
chain become available, but
the insurer is not able to
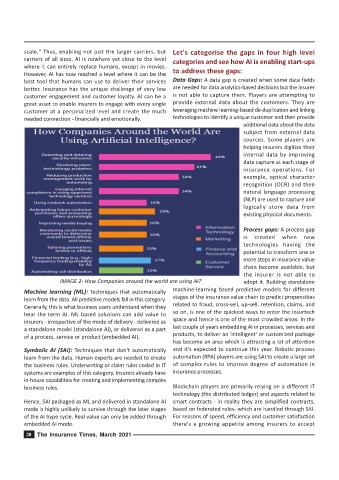
IMAGE 2- How Companies around the world are using AI? adopt it. Building standalone
Machine learning (ML): Techniques that automatically machine-learning based predictive models for different
stages of the insurance value chain to predict propensities
learn from the data. All predictive models fall in this category.
Generally, this is what business users understand when they related to fraud, cross-sell, up-sell, retention, claims, and
so on, is one of the quickest ways to enter the insurtech
hear the term AI. ML based solutions can add value to
insurers - irrespective of the mode of delivery - delivered as space and hence is one of the most crowded areas. In the
a standalone model (standalone AI), or delivered as a part last couple of years embedding AI in processes, services and
products, to deliver an 'intelligent' or customized package
of a process, service or product (embedded AI).
has become an area which is attracting a lot of attention
Symbolic AI (SAI): Techniques that don't automatically and it's expected to continue this year. Robotic process
learn from the data. Human experts are needed to create automation (RPA) players are using SAI to create a large set
the business rules. Underwriting or claim rules coded in IT of complex rules to improve degree of automation in
systems are examples of this category. Insurers already have insurance processes.
in-house capabilities for creating and implementing complex
business rules. Blockchain players are primarily relying on a different IT
technology (the distributed ledger) and aspects related to
Hence, SAI packaged as ML and delivered in standalone AI smart contracts - in reality they are simplified contracts,
mode is highly unlikely to survive through the later stages based on federated rules- which are handled through SAI.
of the AI hype cycle. Real value can only be added through For reasons of speed, efficiency and customer satisfaction
embedded AI mode. there's a growing appetite among insurers to accept
20 The Insurance Times, March 2021