Page 163 - Operations Strategy
P. 163
138 CHAPTER 4 • CAPACiTy sTRATEgy
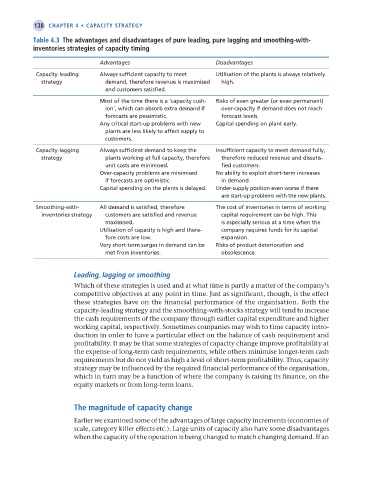
table 4.3 the advantages and disadvantages of pure leading, pure lagging and smoothing-with-
inventories strategies of capacity timing
Advantages Disadvantages
Capacity-leading Always sufficient capacity to meet Utilisation of the plants is always relatively
strategy demand, therefore revenue is maximised high.
and customers satisfied.
Most of the time there is a ‘capacity cush- Risks of even greater (or even permanent)
ion’, which can absorb extra demand if over-capacity if demand does not reach
forecasts are pessimistic. forecast levels.
Any critical start-up problems with new Capital spending on plant early.
plants are less likely to affect supply to
customers.
Capacity-lagging Always sufficient demand to keep the Insufficient capacity to meet demand fully,
strategy plants working at full capacity, therefore therefore reduced revenue and dissatis-
unit costs are minimised. fied customers.
Over-capacity problems are minimised No ability to exploit short-term increases
if forecastsareoptimistic. in demand.
Capital spending on the plants is delayed. Under-supply position even worse if there
are start-up problems with the new plants.
Smoothing-with- All demand is satisfied, therefore The cost of inventories in terms of working
inventories strategy customers are satisfied and revenue capital requirement can be high. This
maximised. is especially serious at a time when the
Utilisation of capacity is high and there- company requires funds for its capital
fore costs are low. expansion.
Very short-term surges in demand can be Risks of product deterioration and
met from inventories. obsolescence.
Leading, lagging or smoothing
Which of these strategies is used and at what time is partly a matter of the company’s
competitive objectives at any point in time. Just as significant, though, is the effect
these strategies have on the financial performance of the organisation. Both the
capacity-leading strategy and the smoothing-with-stocks strategy will tend to increase
the cash requirements of the company through earlier capital expenditure and higher
working capital, respectively. Sometimes companies may wish to time capacity intro-
duction in order to have a particular effect on the balance of cash requirement and
profitability. It may be that some strategies of capacity change improve profitability at
the expense of long-term cash requirements, while others minimise longer-term cash
requirements but do not yield as high a level of short-term profitability. Thus, capacity
strategy may be influenced by the required financial performance of the organisation,
which in turn may be a function of where the company is raising its finance, on the
equity markets or from long-term loans.
the magnitude of capacity change
Earlier we examined some of the advantages of large capacity increments (economies of
scale, category killer effects etc.). Large units of capacity also have some disadvantages
when the capacity of the operation is being changed to match changing demand. If an
M04 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 138 02/03/2017 13:02