Page 213 - Operations Strategy
P. 213
188 CHAPTER 5 • PuRCHAsing And suPPly sTRATEgy
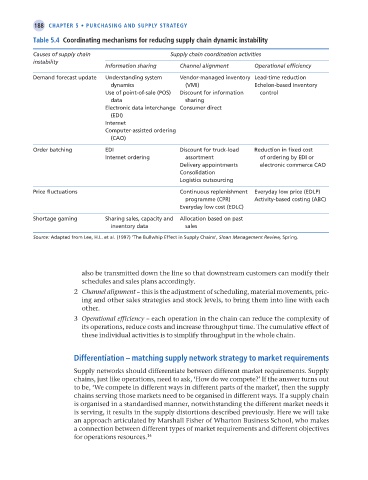
Table 5.4 Coordinating mechanisms for reducing supply chain dynamic instability
Causes of supply chain Supply chain coordination activities
instability
Information sharing Channel alignment Operational efficiency
Demand forecast update Understanding system Vendor-managed inventory Lead-time reduction
dynamics (VMI) Echelon-based inventory
Use of point-of-sale (POS) Discount for information control
data sharing
Electronic data interchange Consumer direct
(EDI)
Internet
Computer-assisted ordering
(CAO)
Order batching EDI Discount for truck-load Reduction in fixed cost
Internet ordering assortment of ordering by EDI or
Delivery appointments electronic commerce CAO
Consolidation
Logistics outsourcing
Price fluctuations Continuous replenishment Everyday low price (EDLP)
programme (CPR) Activity-based costing (ABC)
Everyday low cost (EDLC)
Shortage gaming Sharing sales, capacity and Allocation based on past
inventory data sales
Source: Adapted from Lee, H.L. et al. (1997) ‘The Bullwhip Effect in Supply Chains’, Sloan Management Review, Spring.
also be transmitted down the line so that downstream customers can modify their
schedules and sales plans accordingly.
2 Channel alignment – this is the adjustment of scheduling, material movements, pric-
ing and other sales strategies and stock levels, to bring them into line with each
other.
3 Operational efficiency – each operation in the chain can reduce the complexity of
its operations, reduce costs and increase throughput time. The cumulative effect of
these individual activities is to simplify throughput in the whole chain.
differentiation – matching supply network strategy to market requirements
Supply networks should differentiate between different market requirements. Supply
chains, just like operations, need to ask, ‘How do we compete?’ If the answer turns out
to be, ‘We compete in different ways in different parts of the market’, then the supply
chains serving those markets need to be organised in different ways. If a supply chain
is organised in a standardised manner, notwithstanding the different market needs it
is serving, it results in the supply distortions described previously. Here we will take
an approach articulated by Marshall Fisher of Wharton Business School, who makes
a connection between different types of market requirements and different objectives
for operations resources. 14
M05 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 188 02/03/2017 13:04