Page 300 - Operations Strategy
P. 300
innovATion, dEsign And CREATiviTy 275
prompts a newer, better idea, with each new S-shaped curve requiring some degree of
redesign, see Figure 8.3(b).
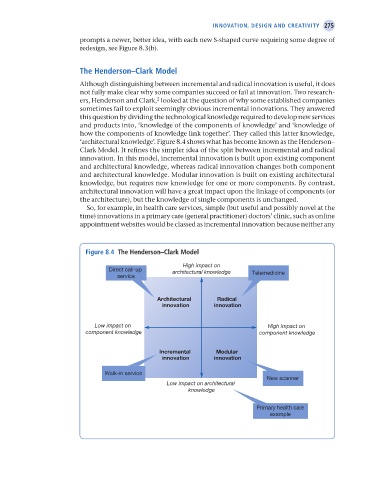
The Henderson–Clark model
Although distinguishing between incremental and radical innovation is useful, it does
not fully make clear why some companies succeed or fail at innovation. Two research-
2
ers, Henderson and Clark, looked at the question of why some established companies
sometimes fail to exploit seemingly obvious incremental innovations. They answered
this question by dividing the technological knowledge required to develop new services
and products into, ‘knowledge of the components of knowledge’ and ‘knowledge of
how the components of knowledge link together’. They called this latter knowledge,
‘architectural knowledge’. Figure 8.4 shows what has become known as the Henderson–
Clark Model. It refines the simpler idea of the split between incremental and radical
innovation. In this model, incremental innovation is built upon existing component
and architectural knowledge, whereas radical innovation changes both component
and architectural knowledge. Modular innovation is built on existing architectural
knowledge, but requires new knowledge for one or more components. By contrast,
architectural innovation will have a great impact upon the linkage of components (or
the architecture), but the knowledge of single components is unchanged.
So, for example, in health care services, simple (but useful and possibly novel at the
time) innovations in a primary care (general practitioner) doctors’ clinic, such as online
appointment websites would be classed as incremental innovation because neither any
Figure 8.4 The Henderson–Clark model
High impact on
Direct call-up architectural knowledge
service Telemedicine
Architectural Radical
innovation innovation
Low impact on High impact on
component knowledge component knowledge
Incremental Modular
innovation innovation
Walk-in service
New scanner
Low impact on architectural
knowledge
Primary health care
example
M08 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 275 02/03/2017 13:07