Page 125 - Libro 2
P. 125
7 — Intracranial Cerebrovascular Examination
105
AB
CD
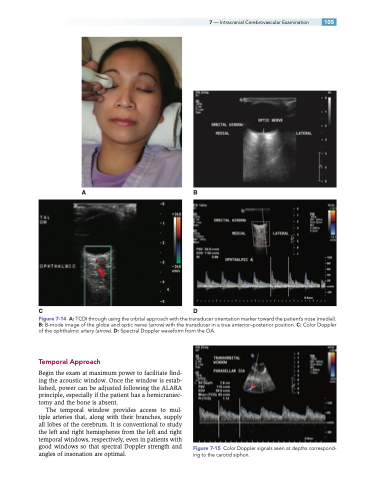
Figure 7-14 A: TCDI through using the orbital approach with the transducer orientation marker toward the patient’s nose (medial). B: B-mode image of the globe and optic nerve (arrow) with the transducer in a true anterior–posterior position. C: Color Doppler of the ophthalmic artery (arrow). D: Spectral Doppler waveform from the OA.
Temporal Approach
Begin the exam at maximum power to facilitate find- ing the acoustic window. Once the window is estab- lished, power can be adjusted following the ALARA principle, especially if the patient has a hemicraniec- tomy and the bone is absent.
The temporal window provides access to mul- tiple arteries that, along with their branches, supply all lobes of the cerebrum. It is conventional to study the left and right hemispheres from the left and right temporal windows, respectively, even in patients with good windows so that spectral Doppler strength and angles of insonation are optimal.
Figure 7-15 Color Doppler signals seen at depths correspond- ing to the carotid siphon.