Page 373 - Libro 2
P. 373
23 — Evaluation of Kidney and Liver Transplants
353
Figure 23-5 Normal spectral Doppler tracing from the origin of the main renal artery. Note the sharp systolic upstroke and continuous forward diastolic flow with an RI 0.70. Mild eleva- tion of the PSV in the main renal artery (204 cm/s) is common secondary to the acute angle of take off from the external iliac artery and increased blood flow through the single vessel.
essential to evaluate for kinking or torquing. Color and spectral Doppler signals are obtained from the main renal vein including the venous anasto- mosis with the external iliac vein (EIV) (Figs. 23-6 and 23-7). A color image and Doppler signal is also
Figure 23-6 Color Doppler image of the renal vein anasto- mosis (arrow).
obtained from the EIV at the level of the anasto- mosis. Spectral tracings should be obtained from the intraparenchymal renal veins at the upper and lower poles. Note that the intraparenchymal renal veins will be found immediately adjacent to the intraparenchymal renal arteries. Color Doppler im- ages demonstrating perfusion of the entire kidney should be obtained with power Doppler images as needed (Fig. 23-8). Perfusion of the renal cortex should be symmetric and homogenous through- out the transplant. Spectral Doppler signals from the segmental and interlobar arteries are obtained from the upper, mid, and lower poles, with angle- corrected peak systolic velocity measurements and calculation of the resistive index (RI). Some laboratories require sampling of the arcuate arteries as well. The normal arterial waveform has a low- resistance pattern characterized by continuous for- ward diastolic flow, an RI less than 0.7, and a sharp systolic upstroke with an acceleration time less than 70 to 80 ms (Fig. 23-9). The RI is a ratio that compares the amount of systolic and diastolic flow.
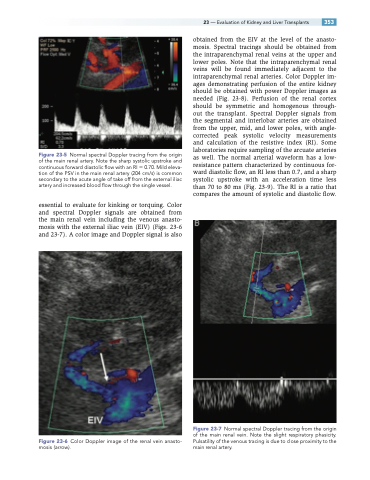
Figure 23-7 Normal spectral Doppler tracing from the origin of the main renal vein. Note the slight respiratory phasicity. Pulsatility of the venous tracing is due to close proximity to the main renal artery.