Page 417 - Libro 2
P. 417
TABLE 26-1
Types of Autogenous Arteriovenous Access
Forearm:
Posterior radial artery to cephalic vein (“snuffbox” fistula) Radial artery to cephalic vein (Brescia-Cimino fistula) Radial artery to cephalic forearm vein transposition
Brachial artery to cephalic forearm vein looped transposition
Radial artery to basilic forearm vein transposition Ulnar artery to basilic forearm vein transposition Brachial artery to basilic forearm vein looped
transposition
Upper arm:
Brachial artery to cephalic vein fistula Brachial artery to basilic vein transposition Brachial artery to brachial vein transposition
Venous Doppler signals from the central veins should display respiratory phasicity, cardiac pulsatility, and augmentation. These characteristics should be used to confirm patency of the central venous system.
26 — Hemodialysis Access Grafts and Fistulae 397 HEMODIALYSISACCESSEVALUATION
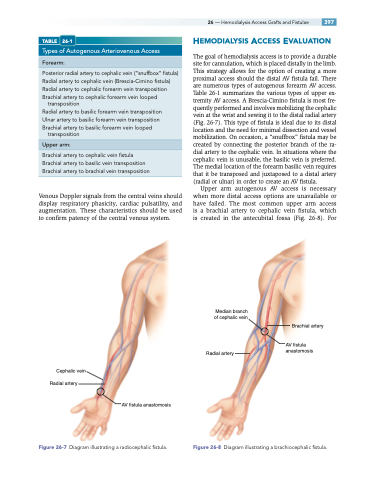
The goal of hemodialysis access is to provide a durable site for cannulation, which is placed distally in the limb. This strategy allows for the option of creating a more proximal access should the distal AV fistula fail. There are numerous types of autogenous forearm AV access. Table 26-1 summarizes the various types of upper ex- tremity AV access. A Brescia-Cimino fistula is most fre- quently performed and involves mobilizing the cephalic vein at the wrist and sewing it to the distal radial artery (Fig. 26-7). This type of fistula is ideal due to its distal location and the need for minimal dissection and vessel mobilization. On occasion, a “snuffbox” fistula may be created by connecting the posterior branch of the ra- dial artery to the cephalic vein. In situations where the cephalic vein is unusable, the basilic vein is preferred. The medial location of the forearm basilic vein requires that it be transposed and juxtaposed to a distal artery (radial or ulnar) in order to create an AV fistula.
Upper arm autogenous AV access is necessary when more distal access options are unavailable or have failed. The most common upper arm access is a brachial artery to cephalic vein fistula, which is created in the antecubital fossa (Fig. 26-8). For
Median branch of cephalic vein
Radial artery
Brachial artery
AV fistula anastomosis
Cephalic vein Radial artery
AV fistula anastomosis
Figure 26-7 Diagram illustrating a radiocephalic fistula.
Figure 26-8 Diagram illustrating a brachiocephalic fistula.