Page 89 - Libro 2
P. 89
5 — Uncommon Pathology of the Carotid System
69
AB
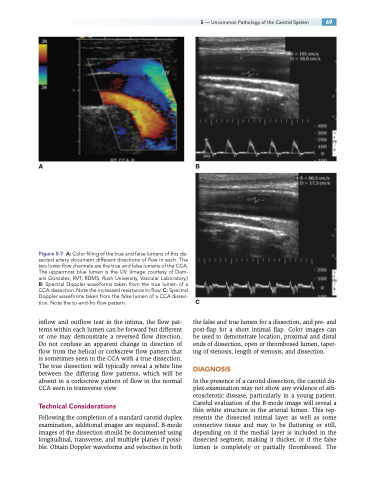
Figure 5-7 A: Color filling of the true and false lumens of this dis- sected artery document different directions of flow in each. The two lower flow channels are the true and false lumens of the CCA. The uppermost blue lumen is the IJV. (Image courtesy of Dam- aris Gonzalez, RVT, RDMS, Rush University, Vascular Laboratory.) B: Spectral Doppler waveforms taken from the true lumen of a CCA dissection. Note the increased resistance to flow. C: Spectral Doppler waveforms taken from the false lumen of a CCA dissec- tion. Note the to-and-fro flow pattern.
inflow and outflow tear in the intima, the flow pat- terns within each lumen can be forward but different or one may demonstrate a reversed flow direction. Do not confuse an apparent change in direction of flow from the helical or corkscrew flow pattern that is sometimes seen in the CCA with a true dissection. The true dissection will typically reveal a white line between the differing flow patterns, which will be absent in a corkscrew pattern of flow in the normal CCA seen in transverse view.
Technical Considerations
Following the completion of a standard carotid duplex examination, additional images are required. B-mode images of the dissection should be documented using longitudinal, transverse, and multiple planes if possi- ble. Obtain Doppler waveforms and velocities in both
C
the false and true lumen for a dissection, and pre- and post-flap for a short intimal flap. Color images can be used to demonstrate location, proximal and distal ends of dissection, open or thrombosed lumen, taper- ing of stenosis, length of stenosis, and dissection.
DIAGNOSIS
In the presence of a carotid dissection, the carotid du- plex examination may not show any evidence of ath- erosclerotic disease, particularly in a young patient. Careful evaluation of the B-mode image will reveal a thin white structure in the arterial lumen. This rep- resents the dissected intimal layer as well as some connective tissue and may to be fluttering or still, depending on if the medial layer is included in the dissected segment, making it thicker, or if the false lumen is completely or partially thrombosed. The