Page 165 - Libro vascular I
P. 165
Chap-11.qxd 29~8~04 14:50 Page 156
156
PERIPHERAL VASCULAR ULTRASOUND
LEAK
R LIMB
AC
GRAFT
LUMBAR
ENDO- LEAK
R
L
SAC
BD
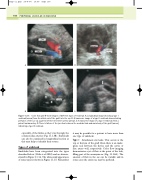
Figure 11.15 Color flow and B-mode images of different types of endoleak. A: Longitudinal image showing a type I endoleak (arrow) from the distal end of the graft into the sac. B: A transverse image of a type II endoleak demonstrating perfusion of the sac via a patent inferior mesenteric artery (arrow). C: A transverse image of a type II endoleak from a patent lumbar artery. D: There is failure of the junction between the modular limb and main body of the graft (arrow), indicating a type III endoleak.
especially of the limbs as they run through the common iliac arteries (Fig. 11.13B). Endoleaks can also be examined in longitudinal section as this may help to identify their source.
Types of endoleak
Endoleaks have been categorized into the types described below (Veith et al 2002) and are demon- strated in Figure 11.14. The ultrasound appearance of some types is shown in Figure 11.15. Remember
it may be possible for a patient to have more than one type of endoleak.
Type I Attachment site leaks. This occurs at the top or bottom of the graft when there is an inade- quate seal between the device and the aortic or iliac artery wall, respectively. Color flow imaging demonstrates a jet of flow at the point of the leak, filling part of the aneurysm sac (Fig. 11.15A). The amount of flow in the sac can be variable and in some cases the entire sac may be perfused.