Page 148 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 148
134 SECTION II Autonomic Drugs
constriction). Ganglionic blockade often causes moderate dilation
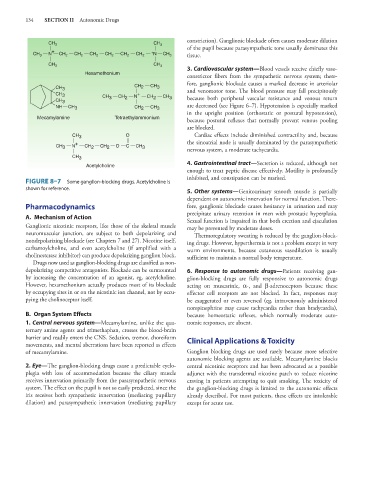
CH 3 CH 3
of the pupil because parasympathetic tone usually dominates this
+ +
N N
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 tissue.
CH 3 CH 3
3. Cardiovascular system—Blood vessels receive chiefly vaso-
Hexamethonium
constrictor fibers from the sympathetic nervous system; there-
fore, ganglionic blockade causes a marked decrease in arteriolar
CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 and venomotor tone. The blood pressure may fall precipitously
CH 3 CH CH N + CH CH because both peripheral vascular resistance and venous return
CH 3 3 2 2 3
NH CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 are decreased (see Figure 6–7). Hypotension is especially marked
in the upright position (orthostatic or postural hypotension),
Mecamylamine Tetraethylammonium
because postural reflexes that normally prevent venous pooling
are blocked.
CH 3 O Cardiac effects include diminished contractility and, because
+ the sinoatrial node is usually dominated by the parasympathetic
CH 3 N CH 2 CH 2 O C CH 3 nervous system, a moderate tachycardia.
CH 3
Acetylcholine 4. Gastrointestinal tract—Secretion is reduced, although not
enough to treat peptic disease effectively. Motility is profoundly
inhibited, and constipation can be marked.
FIGURE 8–7 Some ganglion-blocking drugs. Acetylcholine is
shown for reference.
5. Other systems—Genitourinary smooth muscle is partially
dependent on autonomic innervation for normal function. There-
Pharmacodynamics fore, ganglionic blockade causes hesitancy in urination and may
precipitate urinary retention in men with prostatic hyperplasia.
A. Mechanism of Action Sexual function is impaired in that both erection and ejaculation
Ganglionic nicotinic receptors, like those of the skeletal muscle may be prevented by moderate doses.
neuromuscular junction, are subject to both depolarizing and Thermoregulatory sweating is reduced by the ganglion-block-
nondepolarizing blockade (see Chapters 7 and 27). Nicotine itself, ing drugs. However, hyperthermia is not a problem except in very
carbamoylcholine, and even acetylcholine (if amplified with a warm environments, because cutaneous vasodilation is usually
cholinesterase inhibitor) can produce depolarizing ganglion block. sufficient to maintain a normal body temperature.
Drugs now used as ganglion-blocking drugs are classified as non-
depolarizing competitive antagonists. Blockade can be surmounted 6. Response to autonomic drugs—Patients receiving gan-
by increasing the concentration of an agonist, eg, acetylcholine. glion-blocking drugs are fully responsive to autonomic drugs
However, hexamethonium actually produces most of its blockade acting on muscarinic, α-, and β-adrenoceptors because these
by occupying sites in or on the nicotinic ion channel, not by occu- effector cell receptors are not blocked. In fact, responses may
pying the cholinoceptor itself. be exaggerated or even reversed (eg, intravenously administered
norepinephrine may cause tachycardia rather than bradycardia),
B. Organ System Effects because homeostatic reflexes, which normally moderate auto-
1. Central nervous system—Mecamylamine, unlike the qua- nomic responses, are absent.
ternary amine agents and trimethaphan, crosses the blood-brain
barrier and readily enters the CNS. Sedation, tremor, choreiform Clinical Applications & Toxicity
movements, and mental aberrations have been reported as effects
of mecamylamine. Ganglion blocking drugs are used rarely because more selective
autonomic blocking agents are available. Mecamylamine blocks
2. Eye—The ganglion-blocking drugs cause a predictable cyclo- central nicotinic receptors and has been advocated as a possible
plegia with loss of accommodation because the ciliary muscle adjunct with the transdermal nicotine patch to reduce nicotine
receives innervation primarily from the parasympathetic nervous craving in patients attempting to quit smoking. The toxicity of
system. The effect on the pupil is not so easily predicted, since the the ganglion-blocking drugs is limited to the autonomic effects
iris receives both sympathetic innervation (mediating pupillary already described. For most patients, these effects are intolerable
dilation) and parasympathetic innervation (mediating pupillary except for acute use.