Page 149 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 149
CHAPTER 8 Cholinoceptor-Blocking Drugs 135
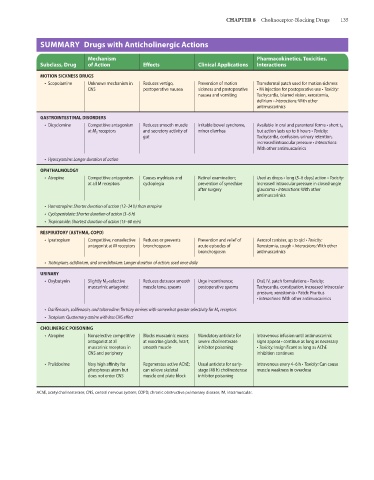
SUMMARY Drugs with Anticholinergic Actions
Mechanism Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities,
Subclass, Drug of Action Effects Clinical Applications Interactions
MOTION SICKNESS DRUGS
• Scopolamine Unknown mechanism in Reduces vertigo, Prevention of motion Transdermal patch used for motion sickness
CNS postoperative nausea sickness and postoperative • IM injection for postoperative use • Toxicity:
nausea and vomiting Tachycardia, blurred vision, xerostomia,
delirium • Interactions: With other
antimuscarinics
GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
• Dicyclomine Competitive antagonism Reduces smooth muscle Irritable bowel syndrome, Available in oral and parenteral forms • short t ½
at M 3 receptors and secretory activity of minor diarrhea but action lasts up to 6 hours • Toxicity:
gut Tachycardia, confusion, urinary retention,
increased intraocular pressure • Interactions:
With other antimuscarinics
• Hyoscyamine: Longer duration of action
OPHTHALMOLOGY
• Atropine Competitive antagonism Causes mydriasis and Retinal examination; Used as drops • long (5–6 days) action • Toxicity:
at all M receptors cycloplegia prevention of synechiae Increased intraocular pressure in closed-angle
after surgery glaucoma • Interactions: With other
antimuscarinics
• Homatropine: Shorter duration of action (12–24 h) than atropine
• Cyclopentolate: Shorter duration of action (3–6 h)
• Tropicamide: Shortest duration of action (15–60 min)
RESPIRATORY (ASTHMA, COPD)
• Ipratropium Competitive, nonselective Reduces or prevents Prevention and relief of Aerosol canister, up to qid • Toxicity:
antagonist at M receptors bronchospasm acute episodes of Xerostomia, cough • Interactions: With other
bronchospasm antimuscarinics
• Tiotropium, aclidinium, and umeclidinium: Longer duration of action; used once daily
URINARY
• Oxybutynin Slightly M 3 -selective Reduces detrusor smooth Urge incontinence; Oral, IV, patch formulations • Toxicity:
muscarinic antagonist muscle tone, spasms postoperative spasms Tachycardia, constipation, increased intraocular
pressure, xerostomia • Patch: Pruritus
• Interactions: With other antimuscarinics
• Darifenacin, solifenacin, and tolterodine: Tertiary amines with somewhat greater selectivity for M 3 receptors
• Trospium: Quaternary amine with less CNS effect
CHOLINERGIC POISONING
• Atropine Nonselective competitive Blocks muscarinic excess Mandatory antidote for Intravenous infusion until antimuscarinic
antagonist at all at exocrine glands, heart, severe cholinesterase signs appear • continue as long as necessary
muscarinic receptors in smooth muscle inhibitor poisoning • Toxicity: Insignificant as long as AChE
CNS and periphery inhibition continues
• Pralidoxime Very high affinity for Regenerates active AChE; Usual antidote for early- Intravenous every 4–6 h • Toxicity: Can cause
phosphorus atom but can relieve skeletal stage (48 h) cholinesterase muscle weakness in overdose
does not enter CNS muscle end plate block inhibitor poisoning
AChE, acetylcholinesterase; CNS, central nervous system; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; IM, intramuscular.