Page 153 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 153
CHAPTER 9 Adrenoceptor Agonists & Sympathomimetic Drugs 139
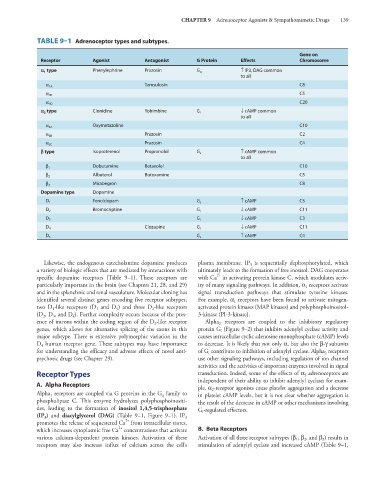
TABLE 9–1 Adrenoceptor types and subtypes.
Gene on
Receptor Agonist Antagonist G Protein Effects Chromosome
` 1 type Phenylephrine Prazosin G q ↑ IP3, DAG common
to all
Tamsulosin C8
α 1A
C5
α 1B
C20
α 1D
` 2 type Clonidine Yohimbine G i ↓ cAMP common
to all
Oxymetazoline C10
α 2A
Prazosin C2
α 2B
Prazosin C4
α 2C
a type Isoproterenol Propranolol G s ↑ cAMP common
to all
Dobutamine Betaxolol C10
β 1
β 2 Albuterol Butoxamine C5
Mirabegron C8
β 3
Dopamine type Dopamine
Fenoldopam ↑ cAMP C5
D 1 G s
Bromocriptine ↓ cAMP C11
D 2 G i
↓ cAMP C3
D 3 G i
D 4 Clozapine G i ↓ cAMP C11
D 5 G s ↑ cAMP C4
Likewise, the endogenous catecholamine dopamine produces plasma membrane. IP is sequentially dephosphorylated, which
3
a variety of biologic effects that are mediated by interactions with ultimately leads to the formation of free inositol. DAG cooperates
2+
specific dopamine receptors (Table 9–1). These receptors are with Ca in activating protein kinase C, which modulates activ-
particularly important in the brain (see Chapters 21, 28, and 29) ity of many signaling pathways. In addition, α receptors activate
1
and in the splanchnic and renal vasculature. Molecular cloning has signal transduction pathways that stimulate tyrosine kinases.
identified several distinct genes encoding five receptor subtypes, For example, α receptors have been found to activate mitogen-
1
two D -like receptors (D and D ) and three D -like receptors activated protein kinases (MAP kinases) and polyphosphoinositol-
5
1
1
2
(D , D , and D ). Further complexity occurs because of the pres- 3-kinase (PI-3-kinase).
3
2
4
ence of introns within the coding region of the D -like receptor Alpha receptors are coupled to the inhibitory regulatory
2
2
genes, which allows for alternative splicing of the exons in this protein G (Figure 9–2) that inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity and
i
major subtype. There is extensive polymorphic variation in the causes intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels
human receptor gene. These subtypes may have importance to decrease. It is likely that not only α, but also the β-γ subunits
D 4
for understanding the efficacy and adverse effects of novel anti- of G contribute to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. Alpha receptors
2
i
psychotic drugs (see Chapter 29). use other signaling pathways, including regulation of ion channel
activities and the activities of important enzymes involved in signal
Receptor Types transduction. Indeed, some of the effects of α 2 adrenoceptors are
independent of their ability to inhibit adenylyl cyclase; for exam-
A. Alpha Receptors ple, α -receptor agonists cause platelet aggregation and a decrease
2
Alpha receptors are coupled via G proteins in the G family to in platelet cAMP levels, but it is not clear whether aggregation is
1
q
phospholipase C. This enzyme hydrolyzes polyphosphoinositi- the result of the decrease in cAMP or other mechanisms involving
des, leading to the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate G i -regulated effectors.
(IP ) and diacylglycerol (DAG) (Table 9–1, Figure 9–1). IP
3
3
2+
promotes the release of sequestered Ca from intracellular stores,
2+
which increases cytoplasmic free Ca concentrations that activate B. Beta Receptors
various calcium-dependent protein kinases. Activation of these Activation of all three receptor subtypes (β , β , and β ) results in
3
1
2
receptors may also increase influx of calcium across the cell’s stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and increased cAMP (Table 9–1,