Page 160 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 160
146 SECTION II Autonomic Drugs
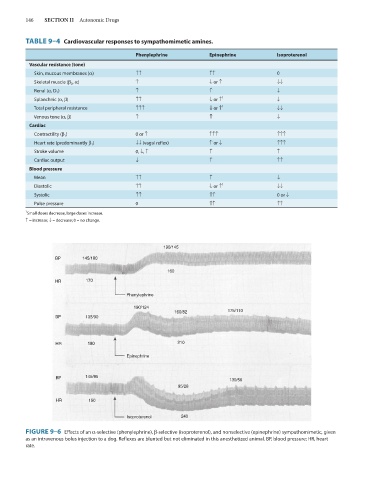
TABLE 9–4 Cardiovascular responses to sympathomimetic amines.
Phenylephrine Epinephrine lsoproterenol
Vascular resistance (tone)
Skin, mucous membranes (α) ↑↑ ↑↑ 0
Skeletal muscle (β 2 , α) ↑ ↓ or ↑ ↓↓
Renal (α, D 1 ) ↑ ↑ ↓
Splanchnic (α, β) ↑↑ ↓ or ↑ 1 ↓
Total peripheral resistance ↑↑↑ ↓ or ↑ 1 ↓↓
Venous tone (α, β) ↑ ↑ ↓
Cardiac
Contractility (β 1 ) 0 or ↑ ↑↑↑ ↑↑↑
Heart rate (predominantly β 1 ) ↓↓ (vagal reflex) ↑ or ↓ ↑↑↑
Stroke volume 0, ↓, ↑ ↑ ↑
Cardiac output ↓ ↑ ↑↑
Blood pressure
Mean ↑↑ ↑ ↓
Diastolic ↑↑ ↓ or ↑ 1 ↓↓
Systolic ↑↑ ↑↑ 0 or ↓
Pulse pressure 0 ↑↑ ↑↑
1 Small doses decrease, large doses increase.
↑ = increase; ↓ = decrease; 0 = no change.
190/145
BP 145/100
160
HR 170
Phenylephrine
190/124
160/82 175/110
BP 135/90
HR 180 210
Epinephrine
BP 145/95
130/50
95/28
HR 150
Isoproterenol 240
FIGURE 9–6 Effects of an α-selective (phenylephrine), β-selective (isoproterenol), and nonselective (epinephrine) sympathomimetic, given
as an intravenous bolus injection to a dog. Reflexes are blunted but not eliminated in this anesthetized animal. BP, blood pressure; HR, heart
rate.