Page 163 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 163
CHAPTER 9 Adrenoceptor Agonists & Sympathomimetic Drugs 149
Norepinephrine (levarterenol, noradrenaline) is an agonist Isoproterenol (isoprenaline) is a very potent β-receptor
at both α and α receptors. Norepinephrine also activates agonist and has little effect on α receptors. The drug has
1
2
β receptors with similar potency as epinephrine, but has positive chronotropic and inotropic actions; because isopro-
1
relatively little effect on β receptors. Consequently, norepi- terenol activates β receptors almost exclusively, it is a potent
2
nephrine increases peripheral resistance and both diastolic and vasodilator. These actions lead to a marked increase in cardiac
systolic blood pressure. Compensatory baroreflex activation output associated with a fall in diastolic and mean arterial
tends to overcome the direct positive chronotropic effects of pressure and a lesser decrease or a slight increase in systolic
norepinephrine; however, the positive inotropic effects on the pressure (Table 9–4; Figure 9–6).
heart are maintained. Beta subtype-selective agonists are very important because
Dopamine is the immediate precursor in the synthesis of the separation of β and β effects (Table 9–2), although incom-
2
1
norepinephrine (see Figure 6–5). Its cardiovascular effects were plete, is sufficient to reduce adverse effects in several clinical
described above. Endogenous dopamine may have more impor- applications.
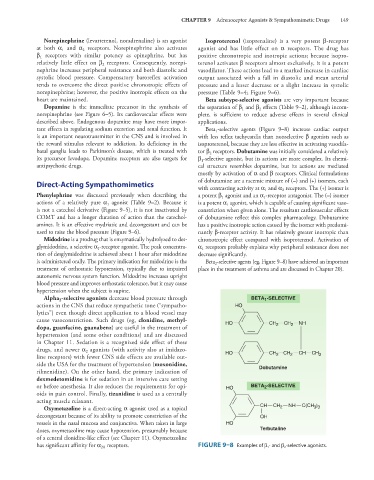
tant effects in regulating sodium excretion and renal function. It Beta -selective agents (Figure 9–8) increase cardiac output
1
is an important neurotransmitter in the CNS and is involved in with less reflex tachycardia than nonselective β agonists such as
the reward stimulus relevant to addiction. Its deficiency in the isoproterenol, because they are less effective in activating vasodila-
basal ganglia leads to Parkinson’s disease, which is treated with tor β receptors. Dobutamine was initially considered a relatively
2
its precursor levodopa. Dopamine receptors are also targets for β -selective agonist, but its actions are more complex. Its chemi-
1
antipsychotic drugs. cal structure resembles dopamine, but its actions are mediated
mostly by activation of α and β receptors. Clinical formulations
Direct-Acting Sympathomimetics of dobutamine are a racemic mixture of (–) and (+) isomers, each
with contrasting activity at α and α receptors. The (+) isomer is
1
2
Phenylephrine was discussed previously when describing the a potent β agonist and an α -receptor antagonist. The (–) isomer
1
1
actions of a relatively pure α agonist (Table 9–2). Because it is a potent α agonist, which is capable of causing significant vaso-
1
1
is not a catechol derivative (Figure 9–5), it is not inactivated by constriction when given alone. The resultant cardiovascular effects
COMT and has a longer duration of action than the catechol- of dobutamine reflect this complex pharmacology. Dobutamine
amines. It is an effective mydriatic and decongestant and can be has a positive inotropic action caused by the isomer with predomi-
used to raise the blood pressure (Figure 9–6). nantly β-receptor activity. It has relatively greater inotropic than
Midodrine is a prodrug that is enzymatically hydrolyzed to des- chronotropic effect compared with isoproterenol. Activation of
glymidodrine, a selective α -receptor agonist. The peak concentra- α receptors probably explains why peripheral resistance does not
1
1
tion of desglymidodrine is achieved about 1 hour after midodrine decrease significantly.
is administered orally. The primary indication for midodrine is the Beta -selective agents (eg, Figure 9–8) have achieved an important
2
treatment of orthostatic hypotension, typically due to impaired place in the treatment of asthma and are discussed in Chapter 20).
autonomic nervous system function. Midodrine increases upright
blood pressure and improves orthostatic tolerance, but it may cause
hypertension when the subject is supine.
Alpha -selective agonists decrease blood pressure through BETA 1 -SELECTIVE
2
actions in the CNS that reduce sympathetic tone (“sympatho- HO
lytics”) even though direct application to a blood vessel may
cause vasoconstriction. Such drugs (eg, clonidine, methyl- HO CH CH NH
dopa, guanfacine, guanabenz) are useful in the treatment of 2 2
hypertension (and some other conditions) and are discussed
in Chapter 11. Sedation is a recognized side effect of these
agonists (with activity also at imidazo-
drugs, and newer α 2 HO CH CH CH CH
line receptors) with fewer CNS side effects are available out- 2 2 3
side the USA for the treatment of hypertension (moxonidine,
rilmenidine). On the other hand, the primary indication of Dobutamine
dexmedetomidine is for sedation in an intensive care setting
or before anesthesia. It also reduces the requirements for opi- HO BETA 2 -SELECTIVE
oids in pain control. Finally, tizanidine is used as a centrally
acting muscle relaxant.
3 3
Oxymetazoline is a direct-acting α agonist used as a topical CH CH 2 NH C(CH )
decongestant because of its ability to promote constriction of the OH
vessels in the nasal mucosa and conjunctiva. When taken in large HO
doses, oxymetazoline may cause hypotension, presumably because Terbutaline
of a central clonidine-like effect (see Chapter 11). Oxymetazoline
has significant affinity for α receptors. FIGURE 9–8 Examples of β 1 - and β 2 -selective agonists.
2A