Page 168 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 168
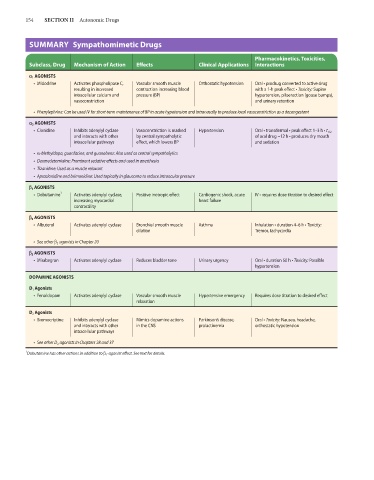
154 SECTION II Autonomic Drugs
SUMMARY Sympathomimetic Drugs
Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities,
Subclass, Drug Mechanism of Action Effects Clinical Applications Interactions
` 1 AGONISTS
• Midodrine Activates phospholipase C, Vascular smooth muscle Orthostatic hypotension Oral • prodrug converted to active drug
resulting in increased contraction increasing blood with a 1-h peak effect • Toxicity: Supine
intracellular calcium and pressure (BP) hypertension, piloerection (goose bumps),
vasoconstriction and urinary retention
• Phenylephrine: Can be used IV for short-term maintenance of BP in acute hypotension and intranasally to produce local vasoconstriction as a decongestant
` 2 AGONISTS
• Clonidine Inhibits adenylyl cyclase Vasoconstriction is masked Hypertension Oral • transdermal • peak effect 1–3 h • t 1/2
and interacts with other by central sympatholytic of oral drug ~12 h • produces dry mouth
intracellular pathways effect, which lowers BP and sedation
• α-Methyldopa, guanfacine, and guanabenz: Also used as central sympatholytics
• Dexmedetomidine: Prominent sedative effects and used in anesthesia
• Tizanidine: Used as a muscle relaxant
• Apraclonidine and brimonidine: Used topically in glaucoma to reduce intraocular pressure
a 1 AGONISTS
• Dobutamine 1 Activates adenylyl cyclase, Positive inotropic effect Cardiogenic shock, acute IV • requires dose titration to desired effect
increasing myocardial heart failure
contractility
a 2 AGONISTS
• Albuterol Activates adenylyl cyclase Bronchial smooth muscle Asthma Inhalation • duration 4–6 h • Toxicity:
dilation Tremor, tachycardia
• See other β 2 agonists in Chapter 20
a 3 AGONISTS
• Mirabegron Activates adenylyl cyclase Reduces bladder tone Urinary urgency Oral • duration 50 h • Toxicity: Possible
hypertension
DOPAMINE AGONISTS
D 1 Agonists
• Fenoldopam Activates adenylyl cyclase Vascular smooth muscle Hypertensive emergency Requires dose titration to desired effect
relaxation
D 2 Agonists
• Bromocriptine Inhibits adenylyl cyclase Mimics dopamine actions Parkinson’s disease, Oral • Toxicity: Nausea, headache,
and interacts with other in the CNS prolactinemia orthostatic hypotension
intracellular pathways
• See other D 2 agonists in Chapters 28 and 37
1
Dobutamine has other actions in addition to β 1 -agonist effect. See text for details.