Page 74 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 74
60 SECTION I Basic Principles
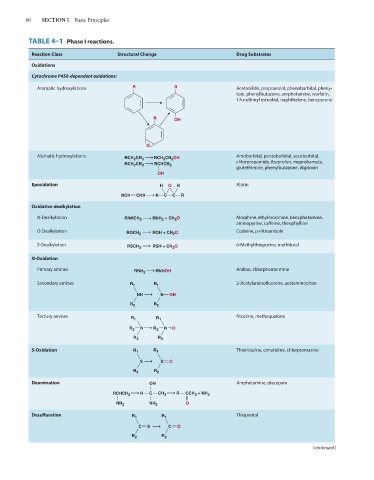
TABLE 4–1 Phase I reactions.
Reaction Class Structural Change Drug Substrates
Oxidations
Cytochrome P450-dependent oxidations:
Aromatic hydroxylations R R Acetanilide, propranolol, phenobarbital, pheny-
toin, phenylbutazone, amphetamine, warfarin,
17α-ethinyl estradiol, naphthalene, benzpyrene
R OH
O
Aliphatic hydroxylations RCH 2 CH 3 RCH 2 CH 2 OH Amobarbital, pentobarbital, secobarbital,
RCH 2 CH 3 RCHCH 3 chlorpropamide, ibuprofen, meprobamate,
glutethimide, phenylbutazone, digitoxin
OH
Epoxidation H O H Aldrin
RCH CHR R C C R
Oxidative dealkylation
N-Dealkylation RNHCH 3 RNH 2 + CH 2 O Morphine, ethylmorphine, benzphetamine,
aminopyrine, ca eine, theophylline
O-Dealkylation Codeine, p-nitroanisole
ROCH 3 ROH + CH 2 O
S-Dealkylation RSCH 3 RSH + CH 2 O 6-Methylthiopurine, methitural
N-Oxidation
Primary amines RNH 2 RNHOH Aniline, chlorphentermine
Secondary amines R 1 R 1 2-Acetylamino uorene, acetaminophen
NH N OH
R 2 R 2
Tertiary amines R 1 R 1 Nicotine, methaqualone
R 2 N R 2 N → O
R 3 R 3
S-Oxidation R 1 R 1 Thioridazine, cimetidine, chlorpromazine
S S O
R 2 R 2
Deamination OH Amphetamine, diazepam
RCHCH 3 R C CH 3 R CCH 3 + NH 3
NH 2 NH 2 O
Desulfuration R 1 R 1 Thiopental
C S C O
R 2 R 2
(continued )