Page 75 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 75
CHAPTER 4 Drug Biotransformation 61
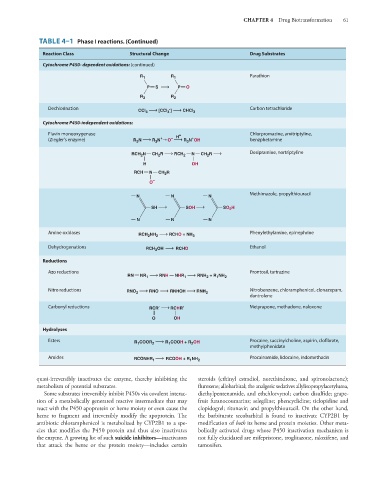
TABLE 4–1 Phase I reactions. (Continued)
Reaction Class Structural Change Drug Substrates
Cytochrome P450- dependent oxidations: (continued)
Parathion
R 1 R 1
P S P O
R 2 R 2
Dechlorination CCl 4 [CCl 3 ] CHCl 3 Carbon tetrachloride
•
Cytochrome P450-independent oxidations:
Flavin monooxygenase + Chlorpromazine, amitriptyline,
+
+
(Ziegler’s enzyme) R N R N → O – H R N OH benzphetamine
3
3
3
RCH N CH R RCH N CH R Desipramine, nortriptyline
2
2
2
2
H OH
RCH N CH R
2
O –
Methimazole, propylthiouracil
N N N
SH SOH SO H
2
N N N
Amine oxidases Phenylethylamine, epinephrine
RCH 2 NH 2 RCHO + NH 3
Dehydrogenations RCH OH RCHO Ethanol
2
Reductions
Azo reductions Prontosil, tartrazine
RN NR 1 RNH NHR 1 RNH + R NH 2
1
2
Nitro reductions RNO 2 RNO RNHOH RNH 2 Nitrobenzene, chloramphenicol, clonazepam,
dantrolene
Carbonyl reductions RCR RCHR Metyrapone, methadone, naloxone
O OH
Hydrolyses
Esters R COOR 2 R COOH + R OH Procaine, succinylcholine, aspirin, clo brate,
2
1
1
methylphenidate
Amides RCONHR 1 RCOOH + R NH 2 Procainamide, lidocaine, indomethacin
1
quasi-irreversibly inactivates the enzyme, thereby inhibiting the steroids (ethinyl estradiol, norethindrone, and spironolactone);
metabolism of potential substrates. fluroxene; allobarbital; the analgesic sedatives allylisopropylacetylurea,
Some substrates irreversibly inhibit P450s via covalent interac- diethylpentenamide, and ethchlorvynol; carbon disulfide; grape-
tion of a metabolically generated reactive intermediate that may fruit furanocoumarins; selegiline; phencyclidine; ticlopidine and
react with the P450 apoprotein or heme moiety or even cause the clopidogrel; ritonavir; and propylthiouracil. On the other hand,
heme to fragment and irreversibly modify the apoprotein. The the barbiturate secobarbital is found to inactivate CYP2B1 by
antibiotic chloramphenicol is metabolized by CYP2B1 to a spe- modification of both its heme and protein moieties. Other meta-
cies that modifies the P450 protein and thus also inactivates bolically activated drugs whose P450 inactivation mechanism is
the enzyme. A growing list of such suicide inhibitors—inactivators not fully elucidated are mifepristone, troglitazone, raloxifene, and
that attack the heme or the protein moiety—includes certain tamoxifen.