Page 228 - Area 9 - Relevant Document
P. 228
85
better conservers of water than exotics. (This is, however, counter to
the desire to produce wood with fast-growing exotics.) Spacing will
depend on species and purpose, but usually no large pieces of land
should be put under trees. Hence, normally a few trees will be planted
at selected places and a fixed spatial arrangement will not be relevant.
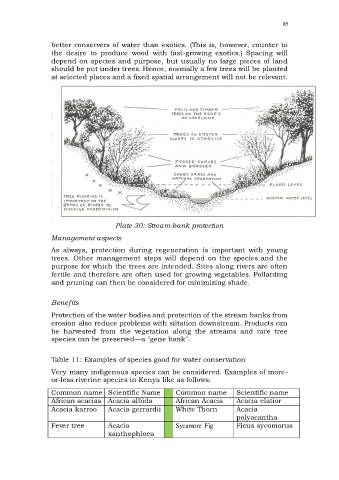
Plate 30: Stream-bank protection
Management aspects
As always, protection during regeneration is important with young
trees. Other management steps will depend on the species and the
purpose for which the trees are intended. Sites along rivers are often
fertile and therefore are often used for growing vegetables. Pollarding
and pruning can then be considered for minimizing shade.
Benefits
Protection of the water bodies and protection of the stream banks from
erosion also reduce problems with siltation downstream. Products can
be harvested from the vegetation along the streams and rare tree
species can be preserved—a "gene bank".
Table 11: Examples of species good for water conservation
Very many indigenous species can be considered. Examples of more-
or-less riverine species in Kenya like as follows:
Common name Scientific Name Common name Scientific name
African acacias Acacia albida African Acacia Acacia elatior
Acacia karroo Acacia gerrardii White Thorn Acacia
polyacantha
Fever tree Acacia Sycamore Fig Ficus sycomorus
xanthophloea