Page 39 - Ilmu Tanah Book
P. 39
26 The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds
by which these elements are released are listed in Table 2.2. The chemical
processes releasing particular nutrient elements are listed in Table 2.3.
Complementing the dissolved nutrient elements in the forms of free ions,
complex ions, and chelates, the soil exchangeable ions are the most easily released
nutrients of the soil solids. The detachment of adsorbed nutrients may progress
through cation exchange described in Eq. 2.6 controlled by K depicted in Eq. 2.7.
This mechanism may quickly supply the nutrient elements in soli water depleted by
plant root absorption. In addition to the related equilibrium constant, there are
some other soil properties controlling this process including soil CEC and pH and
soil solid preferences towards nutrient cations (Table 2.2). The release of nutrient
cations is generally more difficult in soils with high CEC and high pH, particularly for
nutrient cations with high valences that cause high affinities onto the soil solids.
However, low concentration of nutrient cation in soil water may greatly drive their
release from soil solids. Therefore, the absorption of nutrient elements by plant
roots may significantly drive the release of adsorbed nutrient elements. The
+
decrease in soil pH by root excretion of H and organic acids may accelerate the
release of the adsorbed nutrient element.
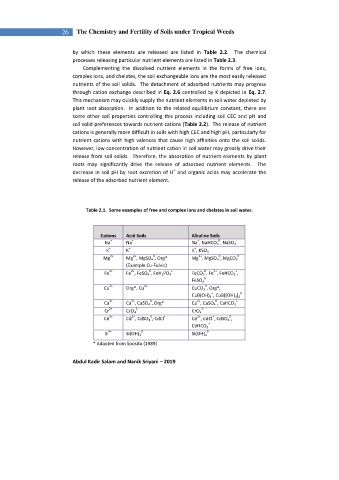
Table 2.1. Some examples of free and complex ions and chelates in soil water.
Cations Acid Soils Alkaline Soils
+
+
0
+
Na Na Na , NaHCO 3 , NaSO 4 -
+
+
+
K K K , KSO 4 -
2+ 2+ 0 2+ 0 0
Mg Mg , MgSO 4 , Org* Mg , MgSO 4 , MgCO 3
(Example Cu-Fulvic)
2+
0
+
+
2+
2+
0
Fe Fe , FeSO 4 , FeH 2 PO 4 FeCO 3 , Fe , FeHCO 3 ,
0
FeSO 4
2+
0
2+
Cu Org*, Cu CuCO 3 , Org*,
0
+
CuB(OH) 4 , CuB[(OH) 4 ] 4
2+ 2+ 0 2+ 0 +
Ca Ca , CaSO 4 , Org* Ca , CaSO 4 , CaHCO 3
2+
2-
2-
Cr CrO 4 CrO 4
2+
+
0
2+
0
+
2+
Cd Cd , CdSO 4 , CdCl Cd , CdCl , CdSO 4 ,
+
CdHCO 3
4+
0
0
Si Si(OH) 4 Si(OH) 4
* Adapted from Sposito (1989)
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019