Page 348 - Programmable Logic Controllers, Fifth Edition - Mobile version
P. 348
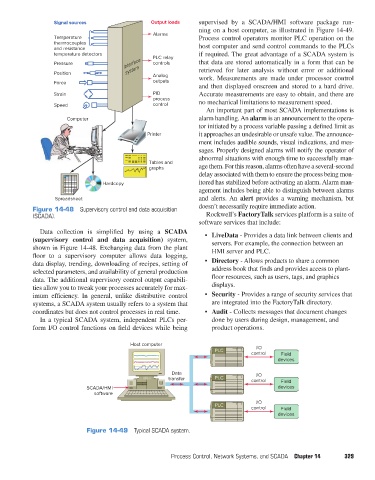
supervised by a SCADA/HMI software package run-
Output loads
Signal sources
ning on a host computer, as illustrated in Figure 14-49.
Alarms
Temperature Process control operators monitor PLC operation on the
thermocouples
and resistance host computer and send control commands to the PLCs
temperature detectors PLC relay if required. The great advantage of a SCADA system is
Interface that data are stored automatically in a form that can be
Pressure controls
Position system Analog retrieved for later analysis without error or additional
work. Measurements are made under processor control
Force outputs
and then displayed onscreen and stored to a hard drive.
Strain PID Accurate measurements are easy to obtain, and there are
process
Speed control no mechanical limitations to measurement speed.
An important part of most SCADA implementations is
Computer alarm handling. An alarm is an announcement to the opera-
tor initiated by a process variable passing a defined limit as
Printer it approaches an undesirable or unsafe value. The announce-
ment includes audible sounds, visual indications, and mes-
sages. Properly designed alarms will notify the operator of
abnormal situations with enough time to successfully man-
Tables and
graphs age them. For this reason, alarms often have a several-second
delay associated with them to ensure the process being mon-
Hardcopy itored has stabilized before activating an alarm. Alarm man-
agement includes being able to distinguish between alarms
Spreadsheet and alerts. An alert provides a warning mechanism, but
Figure 14-48 Supervisory control and data acquisition doesn’t necessarily require immediate action.
(SCADA). Rockwell’s FactoryTalk services platform is a suite of
software services that include:
Data collection is simplified by using a SCADA • LiveData - Provides a data link between clients and
(supervisory control and data acquisition) system, servers. For example, the connection between an
shown in Figure 14-48. Exchanging data from the plant HMI server and PLC.
floor to a supervisory computer allows data logging,
data display, trending, downloading of recipes, setting of • Directory - Allows products to share a common
selected parameters, and availability of general production address book that finds and provides access to plant-
data. The additional supervisory control output capabili- floor resources, such as users, tags, and graphics
ties allow you to tweak your processes accurately for max- displays.
imum efficiency. In general, unlike distributive control • Security - Provides a range of security services that
systems, a SCADA system usually refers to a system that are integrated into the FactoryTalk directory.
coordinates but does not control processes in real time. • Audit - Collects messages that document changes
In a typical SCADA system, independent PLCs per- done by users during design, management, and
form I/O control functions on field devices while being product operations.
Host computer I/O
PLC
control Field
devices
Data I/O
transfer PLC control Field
SCADA/HMI devices
software
I/O
PLC
control Field
devices
Figure 14-49 Typical SCADA system.
Process Control, Network Systems, and SCADA Chapter 14 329
pet73842_ch14_305-332.indd 329 05/11/15 4:29 PM