Page 42 - Programmable Logic Controllers, Fifth Edition - Mobile version
P. 42
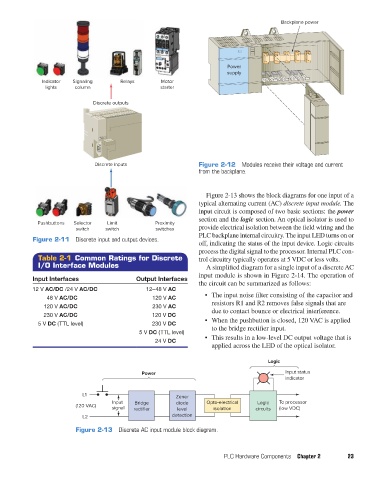
Power Backplane power
supply
Indicator Signaling Relays Motor
lights column starter
Discrete outputs
Discrete inputs Figure 2-12 Modules receive their voltage and current
from the backplane.
Figure 2-13 shows the block diagrams for one input of a
typical alternating current (AC) discrete input module. The
input circuit is composed of two basic sections: the power
section and the logic section. An optical isolator is used to
Pushbuttons Selector Limit Proximity
switch switch switches provide electrical isolation between the field wiring and the
PLC backplane internal circuitry. The input LED turns on or
Figure 2-11 Discrete input and output devices.
off, indicating the status of the input device. Logic circuits
process the digital signal to the processor. Internal PLC con-
Table 2-1 Common Ratings for Discrete trol circuitry typically operates at 5 VDC or less volts.
I/O Interface Modules A simplified diagram for a single input of a discrete AC
input module is shown in Figure 2-14. The operation of
Input Interfaces Output Interfaces
the circuit can be summarized as follows:
12 V AC/DC /24 V AC/DC 12–48 V AC
48 V AC/DC 120 V AC • The input noise filter consisting of the capacitor and
120 V AC/DC 230 V AC resistors R1 and R2 removes false signals that are
230 V AC/DC 120 V DC due to contact bounce or electrical interference.
5 V DC (TTL level) 230 V DC • When the pushbutton is closed, 120 VAC is applied
5 V DC (TTL level) to the bridge rectifier input.
24 V DC • This results in a low-level DC output voltage that is
applied across the LED of the optical isolator.
Logic
Power Input status
indicator
L1 Zener
Input Bridge diode Opto-electrical Logic To processor
(120 VAC) signal rectifier level isolation circuits (low VDC)
L2 detection
Figure 2-13 Discrete AC input module block diagram.
PLC Hardware Components Chapter 2 23
pet73842_ch02_017-045.indd 23 03/11/15 3:43 PM