Page 68 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 68
c02demandandsupplyanalysis.qxd 6/14/10 1:39 PM Page 42
42 CHAPTER 2 DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
6
over time. Briefly, every six months the BLS finds new puter. Along similar lines, many new uses for com-
computer components or peripherals with functional- puters were introduced over time. In addition, con-
ity similar to those used to construct the most recent sumers became more educated in how to use com-
computer price estimate. The price of the new compo- puters, increasing their productivity from using
nents is then used to produce a new estimated com- them.
puter price. We know that an increase in demand, holding
Figure 2.13 shows an incredible decline in com- the supply curve fixed, should cause the equilibrium
puter prices over time. A computer bought in mid- price to rise. That computer prices fell indicates that
1990 would cost about one-tenth of what a com- something other than the demand curve must have
puter with similar capabilities would have cost 20 shifted. Figure 2.14 shows that the pattern of ob-
years before! If data on quality-adjusted prices were served priced and quantities is consistent with a
available going back to when Microsoft was simultaneous rightward shift of both the demand
founded in 1975, we would see similar trends. At the and supply curves.
same time, the total quantity of computers sold What caused the increase in supply for comput-
grew many times over. What explains this pattern of ers? The most important effect was “Moore’s Law”
prices and quantities? (named after Intel co-founder Gordon Moore, who
7
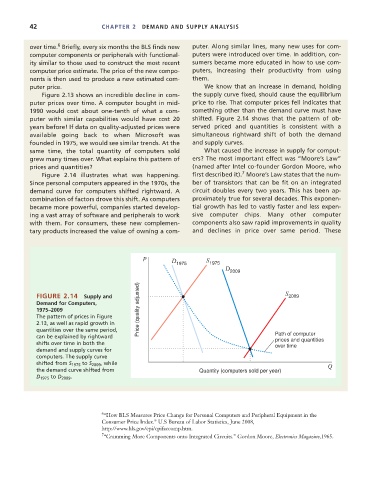
Figure 2.14 illustrates what was happening. first described it). Moore’s Law states that the num-
Since personal computers appeared in the 1970s, the ber of transistors that can be fit on an integrated
demand curve for computers shifted rightward. A circuit doubles every two years. This has been ap-
combination of factors drove this shift. As computers proximately true for several decades. This exponen-
became more powerful, companies started develop- tial growth has led to vastly faster and less expen-
ing a vast array of software and peripherals to work sive computer chips. Many other computer
with them. For consumers, these new complemen- components also saw rapid improvements in quality
tary products increased the value of owning a com- and declines in price over same period. These
P D S
1975 1975
D
2009
FIGURE 2.14 Supply and S 2009
Demand for Computers,
1975–2009 Price (quality adjusted)
The pattern of prices in Figure
2.13, as well as rapid growth in
quantities over the same period, Path of computer
can be explained by rightward prices and quantities
shifts over time in both the over time
demand and supply curves for
computers. The supply curve
shifted from S 1975 to S 2009 , while Q
the demand curve shifted from Quantity (computers sold per year)
D 1975 to D 2009 .
6 “How BLS Measures Price Change for Personal Computers and Peripheral Equipment in the
Consumer Price Index.” U.S Bureau of Labor Statistics, June 2008,
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/cpifaccomp.htm.
7 “Cramming More Components onto Integrated Circuits.” Gordon Moore, Electronics Magazine,1965.