Page 70 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 70
c02demandandsupplyanalysis.qxd 6/14/10 1:39 PM Page 44
44 CHAPTER 2 DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
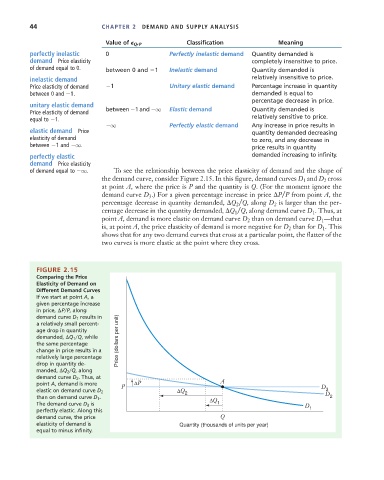
Value of Q , P Classification Meaning
perfectly inelastic 0 Perfectly inelastic demand Quantity demanded is
demand Price elasticity completely insensitive to price.
of demand equal to 0. between 0 and 1 Inelastic demand Quantity demanded is
inelastic demand relatively insensitive to price.
Price elasticity of demand 1 Unitary elastic demand Percentage increase in quantity
between 0 and 1. demanded is equal to
percentage decrease in price.
unitary elastic demand
Price elasticity of demand between 1 and q Elastic demand Quantity demanded is
equal to 1. relatively sensitive to price.
q Perfectly elastic demand Any increase in price results in
elastic demand Price quantity demanded decreasing
elasticity of demand to zero, and any decrease in
between 1 and q.
price results in quantity
perfectly elastic demanded increasing to infinity.
demand Price elasticity
of demand equal to q. To see the relationship between the price elasticity of demand and the shape of
the demand curve, consider Figure 2.15. In this figure, demand curves D 1 and D 2 cross
at point A, where the price is P and the quantity is Q. (For the moment ignore the
demand curve D 3 .) For a given percentage increase in price PP from point A, the
percentage decrease in quantity demanded, Q 2 Q, along D 2 is larger than the per-
centage decrease in the quantity demanded, Q 1 Q, along demand curve D 1 . Thus, at
point A, demand is more elastic on demand curve D 2 than on demand curve D 1 ––that
is, at point A, the price elasticity of demand is more negative for D 2 than for D 1 . This
shows that for any two demand curves that cross at a particular point, the flatter of the
two curves is more elastic at the point where they cross.
FIGURE 2.15
Comparing the Price
Elasticity of Demand on
Different Demand Curves
If we start at point A, a
given percentage increase
in price, ¢P P , along
demand curve D 1 results in
a relatively small percent-
age drop in quantity
demanded, Q 1 Q, while
the same percentage Price (dollars per unit)
change in price results in a
relatively large percentage
drop in quantity de-
manded, Q 2 Q, along
demand curve D 2 . Thus, at
point A, demand is more ΔP A
P D
3
elastic on demand curve D 2 ΔQ 2 D
than on demand curve D 1 . ΔQ 2
The demand curve D 3 is 1 D
perfectly elastic. Along this 1
demand curve, the price Q
elasticity of demand is Quantity (thousands of units per year)
equal to minus infinity.