Page 367 - Handbook of Modern Telecommunications
P. 367
3-158 CRC Handbook of Modern Telecommunications, Second Edition
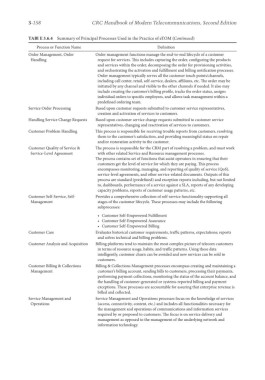
TABl E 3.6.4 Summary of Principal Processes Used in the Practice of eTOM (Continued)
Process or Function Name Definition
Order Management, Order Order management functions manage the end-to-end lifecycle of a customer
Handling request for services. This includes capturing the order, configuring the products
and services within the order, decomposing the order for provisioning activities,
and orchestrating the activation and fulfillment and billing notification processes.
Order management typically serves all the customer touch points/channels,
including call center, retail, self-service, dealers, affiliates, etc. The order may be
initiated by any channel and visible to the other channels if needed. It also may
include creating the customer’s billing profile, tracks the order status, assigns
individual orders to specific employees, and allows task management within a
predefined ordering team.
Service Order Processing Based upon customer requests submitted to customer service representatives,
creation and activation of services to customers.
Handling Service Change Requests Based upon customer service change requests submitted to customer service
representatives, changing and reactivation of services to customers.
Customer Problem Handling This process is responsible for receiving trouble reports from customers, resolving
them to the customer’s satisfaction, and providing meaningful status on repair
and/or restoration activity to the customer.
Customer Quality of Service & The process is responsible for the CRM part of resolving a problem, and must work
Service-Level Agreement with other related Service and Resource management processes.
The process contains set of functions that assist operators in ensuring that their
customers get the level of service for which they are paying. This process
encompasses monitoring, managing, and reporting of quality of service (QoS),
service-level agreements, and other service-related documents. Outputs of this
process are standard (predefined) and exception reports including, but not limited
to, dashboards, performance of a service against a SLA, reports of any developing
capacity problems, reports of customer usage patterns, etc.
Customer Self-Service, Self- Provides a comprehensive collection of self-service functionality supporting all
Management stages of the customer lifecycle. These processes may include the following
subprocesses:
• Customer Self-Empowered Fulfillment
• Customer Self-Empowered Assurance
• Customer Self-Empowered Billing
Customer Care Evaluates historical customer requirements, traffic patterns, expectations; reports
and solves technical and billing problems.
Customer Analysis and Acquisition Billing platforms tend to maintain the most complex picture of telecom customers
in terms of resource usage, habits, and traffic patterns. Using these data
intelligently, customer churn can be avoided and new services can be sold to
customers.
Customer Billing & Collections Billing & Collections Management processes encompass creating and maintaining a
Management customer’s billing account, sending bills to customers, processing their payments,
performing payment collections, monitoring the status of the account balance, and
the handling of customer-generated or systems-reported billing and payment
exceptions. These processes are accountable for assuring that enterprise revenue is
billed and collected.
Service Management and Service Management and Operations processes focus on the knowledge of services
Operations (access, connectivity, content, etc.) and includes all functionalities necessary for
the management and operations of communications and information services
required by or proposed to customers. The focus is on service delivery and
management as opposed to the management of the underlying network and
information technology.