Page 556 - Handbook of Modern Telecommunications
P. 556
Network Organization and Governance 4-87
Company Network
Company
Site A CE PE
Service Peering Service
Provider A Point Provider B
Company
PE CE
Site B
Administration boundary Administration boundary
SPOP SPOP
CE Customer edge router
PE Provider edge router
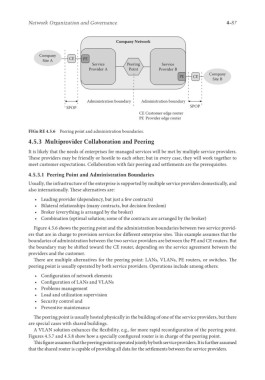
FIGu RE 4.5.6 Peering point and administration boundaries.
4.5.3 Multiprovider Collaboration and Peering
It is likely that the needs of enterprises for managed services will be met by multiple service providers.
These providers may be friendly or hostile to each other; but in every case, they will work together to
meet customer expectations. Collaboration with fair peering and settlements are the prerequisites.
4.5.3.1 Peering Point and Administration Boundaries
Usually, the infrastructure of the enterprise is supported by multiple service providers domestically, and
also internationally. These alternatives are:
• Leading provider (dependency, but just a few contracts)
• Bilateral relationships (many contracts, but decision freedom)
• Broker (everything is arranged by the broker)
• Combination (optimal solution; some of the contracts are arranged by the broker)
Figure 4.5.6 shows the peering point and the administration boundaries between two service provid-
ers that are in charge to provision services for different enterprise sites. This example assumes that the
boundaries of administration between the two service providers are between the PE and CE routers. But
the boundary may be shifted toward the CE router, depending on the service agreement between the
providers and the customer.
There are multiple alternatives for the peering point: LANs, VLANs, PE routers, or switches. The
peering point is usually operated by both service providers. Operations include among others:
• Configuration of network elements
• Configuration of LANs and VLANs
• Problems management
• Load and utilization supervision
• Security control and
• Preventive maintenance
The peering point is usually hosted physically in the building of one of the service providers, but there
are special cases with shared buildings.
A VLAN solution enhances the flexibility, e.g., for more rapid reconfiguration of the peering point.
Figures 4.5.7 and 4.5.8 show how a specially configured router is in charge of the peering point.
This figure assumes that the peering point is operated jointly by both service providers. It is further assumed
that the shared router is capable of providing all data for the settlements between the service providers.