Page 557 - Handbook of Modern Telecommunications
P. 557
4-88 CRC Handbook of Modern Telecommunications, Second Edition
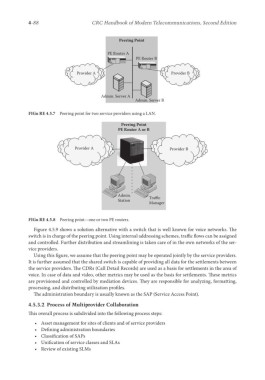
Peering Point
PE Router A
PE Router B
Provider A Provider B
Admin. Server A
Admin. Server B
FIGu RE 4.5.7 Peering point for two service providers using a LAN.
Peering Point
PE Router A or B
Provider A Provider B
Admin. Traffic
Station
Manager
FIGu RE 4.5.8 Peering point—one or two PE routers.
Figure 4.5.9 shows a solution alternative with a switch that is well known for voice networks. The
switch is in charge of the peering point. Using internal addressing schemes, traffic flows can be assigned
and controlled. Further distribution and streamlining is taken care of in the own networks of the ser-
vice providers.
Using this figure, we assume that the peering point may be operated jointly by the service providers.
It is further assumed that the shared switch is capable of providing all data for the settlements between
the service providers. The CDRs (Call Detail Records) are used as a basis for settlements in the area of
voice. In case of data and video, other metrics may be used as the basis for settlements. These metrics
are provisioned and controlled by mediation devices. They are responsible for analyzing, formatting,
processing, and distributing utilization profiles.
The administration boundary is usually known as the SAP (Service Access Point).
4.5.3.2 Process of Multiprovider Collaboration
This overall process is subdivided into the following process steps:
• Asset management for sites of clients and of service providers
• Defining administration boundaries
• Classification of SAPs
• Unification of service classes and SLAs
• Review of existing SLMs