Page 547 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 547
Distillation
column
Boiling temp. Product
Less than 5ºC
Butane
20–180ºC
Naphtha
20–200ºC
Gasoline
Crude oil 180–260ºC
Kerosene
260–340ºC
Diesel
300–370ºC
Lubricating oil
370–600ºC
Fuel oil
(a) Distillation columns
Boiler
Residue
(b) Distillation process
Gasoline (48.5%)
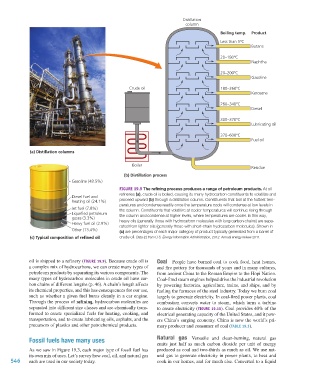
FIGURE 19.9 The refining process produces a range of petroleum products. At oil
refineries (a), crude oil is boiled, causing its many hydrocarbon constituents to volatilize and
Diesel fuel and
heating oil (24.1%) proceed upward (b) through a distillation column. Constituents that boil at the hottest tem-
peratures and condense readily once the temperature cools will condense at low levels in
Jet fuel (7.8%) the column. Constituents that volatilize at cooler temperatures will continue rising through
Liquefied petroleum the column and condense at higher levels, where temperatures are cooler. In this way,
gases (3.3%)
Heavy fuel oil (2.9%) heavy oils (generally those with hydrocarbon molecules with long carbon chains) are sepa-
rated from lighter oils (generally those with short-chain hydrocarbon molecules). Shown in
Other (13.4%) (c) are percentages of each major category of product typically generated from a barrel of
(c) Typical composition of refined oil crude oil. Data (c) from U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2012. Annual energy review 2011.
oil is shipped to a refinery (FIGURE 19.9). Because crude oil is Coal People have burned coal to cook food, heat homes,
a complex mix of hydrocarbons, we can create many types of and fire pottery for thousands of years and in many cultures,
petroleum products by separating its various components. The from ancient China to the Roman Empire to the Hopi Nation.
many types of hydrocarbon molecules in crude oil have car- Coal-fired steam engines helped drive the industrial revolution
bon chains of different lengths (p. 46). A chain’s length affects by powering factories, agriculture, trains, and ships, and by
its chemical properties, and this has consequences for our use, fueling the furnaces of the steel industry. Today we burn coal
such as whether a given fuel burns cleanly in a car engine. largely to generate electricity. In coal-fired power plants, coal
Through the process of refining, hydrocarbon molecules are combustion converts water to steam, which turns a turbine
separated into different size classes and are chemically trans- to create electricity (FIGURE 19.10). Coal provides 40% of the
formed to create specialized fuels for heating, cooking, and electrical generating capacity of the United States, and it pow-
transportation, and to create lubricating oils, asphalts, and the ers China’s surging economy. China is now the world’s pri-
precursors of plastics and other petrochemical products. mary producer and consumer of coal (TABLE 19.3).
Fossil fuels have many uses Natural gas Versatile and clean-burning, natural gas
emits just half as much carbon dioxide per unit of energy
As we saw in Figure 19.3, each major type of fossil fuel has produced as coal and two-thirds as much as oil. We use nat-
its own mix of uses. Let’s survey how coal, oil, and natural gas ural gas to generate electricity in power plants, to heat and
546 each are used in our society today. cook in our homes, and for much else. Converted to a liquid
M19_WITH7428_05_SE_C19.indd 546 12/12/14 5:22 PM