Page 632 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 632
FIGURE 22.5 Since the 1980s,
250 Recovery for composting recycling and composting
U.S. municipal solid waste (millions of tons) 150 Combustion has declined. As of 2010, 54%
have grown in the United
States; as a result, the propor-
Recovery for recycling
200
tion of waste going to landfills
Landfill, other disposal
of U.S. municipal solid waste went
to landfills and 12% to incinera-
tors, whereas 34% was recovered
for composting and recycling.
100
Data from U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency, 2011. Municipal solid waste
generation, recycling, and disposal in the
United States: Facts and figures for 2010.
50
EPA, Washington, D.C.
Has the amount of solid
0 waste that is combusted
1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 (incinerated) increased or
Year decreased since 1960?
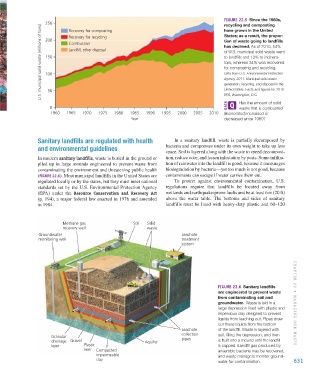
Sanitary landfills are regulated with health In a sanitary landfill, waste is partially decomposed by
and environmental guidelines bacteria and compresses under its own weight to take up less
space. Soil is layered along with the waste to speed decomposi-
In modern sanitary landfills, waste is buried in the ground or tion, reduce odor, and lessen infestation by pests. Some infiltra-
piled up in large mounds engineered to prevent waste from tion of rainwater into the landfill is good, because it encourages
contaminating the environment and threatening public health biodegradation by bacteria—yet too much is not good, because
(FIGURE 22.6). Most municipal landfills in the United States are contaminants can escape if water carries them out.
regulated locally or by the states, but they must meet national To protect against environmental contamination, U.S.
standards set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulations require that landfills be located away from
(EPA) under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act wetlands and earthquake-prone faults and be at least 6 m (20 ft)
(p. 194), a major federal law enacted in 1976 and amended above the water table. The bottoms and sides of sanitary
in 1984. landfills must be lined with heavy-duty plastic and 60–120
Methane gas Soil Solid
recovery well waste
Groundwater Leachate
monitoring well treatment
system
FIGURE 22.6 Sanitary landfills
are engineered to prevent waste
from contaminating soil and
groundwater. Waste is laid in a CHAPTER 22 • MAN A GING OUR WASTE
large depression lined with plastic and
impervious clay designed to prevent
liquids from leaching out. Pipes draw
out these liquids from the bottom
Leachate of the landfill. Waste is layered with
collection soil, filling the depression, and then
Granular pipes
drainage Gravel Aquifer is built into a mound until the landfill
layer Plastic is capped. Landfill gas produced by
liner Compacted anaerobic bacteria may be recovered,
impermeable and waste managers monitor ground-
clay 631
water for contamination.
M22_WITH7428_05_SE_C22.indd 631 13/12/14 2:25 PM