Page 708 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 708
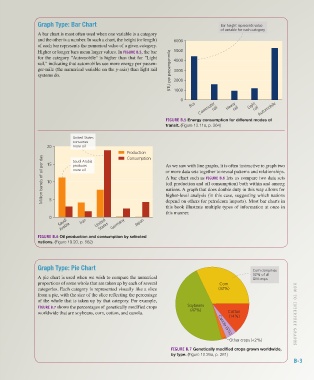
Graph Type: Bar Chart Bar height represents value
of variable for each category
A bar chart is most often used when one variable is a category
and the other is a number. In such a chart, the height (or length) 6000
of each bar represents the numerical value of a given category.
Higher or longer bars mean larger values. In FIGURE B.5, the bar 5000
for the category "Automobile" is higher than that for "Light 4000
rail," indicating that automobiles use more energy per passen-
ger-mile (the numerical variable on the y-axis) than light rail BTU per passenger-mile 3000
systems do. 2000
1000
0
Commuter rail rail rail Automobile
Bus Heavy Light
FIGURE B.5 Energy consumption for different modes of
transit. (Figure 13.11a, p. 364)
United States
consumes
20 more oil
Production As we saw with line graphs, it is often instructive to graph two
Million barrels of oil per day 10 more oil or more data sets together to reveal patterns and relationships.
Consumption
Saudi Arabia
15
produces
A bar chart such as FIGURE B.6 lets us compare two data sets
(oil production and oil consumption) both within and among
nations. A graph that does double duty in this way allows for
higher-level analysis (in this case, suggesting which nations
5
depend on others for petroleum imports). Most bar charts in
this book illustrate multiple types of information at once in
this manner.
0
Saudi Iran United Germany Japan
States
Arabia
FIGURE B.6 Oil production and consumption by selected
nations. (Figure 19.20, p. 562)
Graph Type: Pie Chart Corn comprises
32% of all
A pie chart is used when we wish to compare the numerical GM crops
proportions of some whole that are taken up by each of several Corn
categories. Each category is represented visually like a slice (32%)
from a pie, with the size of the slice reflecting the percentage
of the whole that is taken up by that category. For example,
FIGURE B.7 shows the percentages of genetically modified crops Soybeans
worldwide that are soybeans, corn, cotton, and canola. (47%) Cotton
(14%) H O W T O INTERPRET GRAPH S
Canola (5%)
Other crops (<2%)
FIGURE B.7 Genetically modified crops grown worldwide,
by type. (Figure 10.26a, p. 281)
B-3
Z02_WITH7428_05_SE_AppB.indd 3 13/12/14 10:51 AM