Page 340 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 340
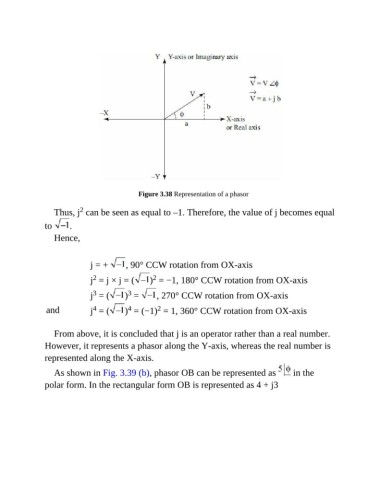
Figure 3.38 Representation of a phasor
2
Thus, j can be seen as equal to –1. Therefore, the value of j becomes equal
to .
Hence,
j = + , 90° CCW rotation from OX-axis
2
2
j = j × j = ( ) = −1, 180° CCW rotation from OX-axis
3
3
j = ( ) = , 270° CCW rotation from OX-axis
4
2
4
and j = ( ) = (−1) = 1, 360° CCW rotation from OX-axis
From above, it is concluded that j is an operator rather than a real number.
However, it represents a phasor along the Y-axis, whereas the real number is
represented along the X-axis.
As shown in Fig. 3.39 (b), phasor OB can be represented as in the
polar form. In the rectangular form OB is represented as 4 + j3