Page 357 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 357
Example 3.20 In an L–R–C series circuit the voltage drops across the
resistor, inductor, and capacitor are 20 V, 60 V, and 30 V, respectively.
Calculate the magnitude of the applied voltage and the power factor of the
circuit.
Solution:
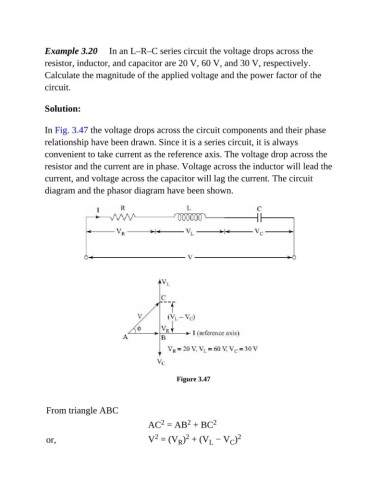
In Fig. 3.47 the voltage drops across the circuit components and their phase
relationship have been drawn. Since it is a series circuit, it is always
convenient to take current as the reference axis. The voltage drop across the
resistor and the current are in phase. Voltage across the inductor will lead the
current, and voltage across the capacitor will lag the current. The circuit
diagram and the phasor diagram have been shown.
Figure 3.47
From triangle ABC
2
2
AC = AB + BC 2
2
2
or, V = (V ) + (V − V ) 2
C
L
R